Grid Trading vs DCA: Which Crypto Bot Strategy Works Best in Bear Markets?

Contents
- Introduction
- What is Grid Trading?
- What is DCA in Cryptocurrency?
- Grid Trading vs DCA: Comparative Analysis
- Practical Recommendations
- Conclusion
Introduction
A bear market in cryptocurrencies is often characterised by high volatility and a decline in the prices of most assets. In such conditions, investors and traders face the challenge of choosing the most resilient strategy.
Among the popular approaches are grid trading and DCA (Dollar Cost Averaging)—methods often implemented through automated trading bots. By understanding the mechanics of these strategies and their applicability in a falling market, one can determine which tool is more effective for different types of participants.
What is Grid Trading?

Grid trading is a method where a trading bot places a series of buy and sell orders within a predefined price range. As market prices fluctuate, the corresponding orders are triggered, allowing profits to be made even from small market movements.
How Grid Trading Works
The mechanics are based on dividing a price range into “grids”:
-
The bot places pending buy orders below the current price and sell orders above it
-
When the price drops, buy orders are executed; when it rises, sell orders are triggered
-
Each completed cycle generates profit from the price difference
This approach can be viewed as a strategy that capitalises on market volatility: the more fluctuations, the higher the potential returns.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Grid Trading
Grid trading has both strengths and significant risks.
Advantages:
-
Ability to profit from fluctuations even in a sideways market
-
Full automation through a trading bot
-
Flexibility in setting the price range and number of orders
Disadvantages:
-
Vulnerability to prolonged trends
-
Challenges in capital management during sharp price movements
-
Risk of low returns in the absence of volatility
What is DCA in Cryptocurrency?
DCA (Dollar Cost Averaging) is a strategy of averaging the cost of purchases. An investor regularly buys an asset for a fixed amount, regardless of its current price. This method is often chosen by long-term investors who view cryptocurrency as a wealth-building tool.
How the DCA Strategy Works
The core principle lies in disciplined and consistent investments:
-
Regular purchases of a fixed amount (e.g., weekly or monthly)
-
Minimising the impact of short-term price fluctuations
-
Establishing an average purchase price over a long period
The DCA strategy does not require chart analysis or market forecasting, making it convenient for beginners. It can also be used for selling in a bull market, helping to capitalise on strong price growth and establish an average selling price.
Pros and Cons of DCA
The averaging strategy has notable strengths and limitations.
Advantages:
-
Reduced emotional stress for the investor
-
Consistent asset accumulation regardless of market trends
-
Lower risk of buying an asset at an inflated price
Disadvantages:
-
Reduced effectiveness during prolonged market declines
-
Lack of quick profits in volatile conditions
-
Dependence on the long-term growth of the cryptocurrency
Grid Trading vs DCA: Comparative Analysis
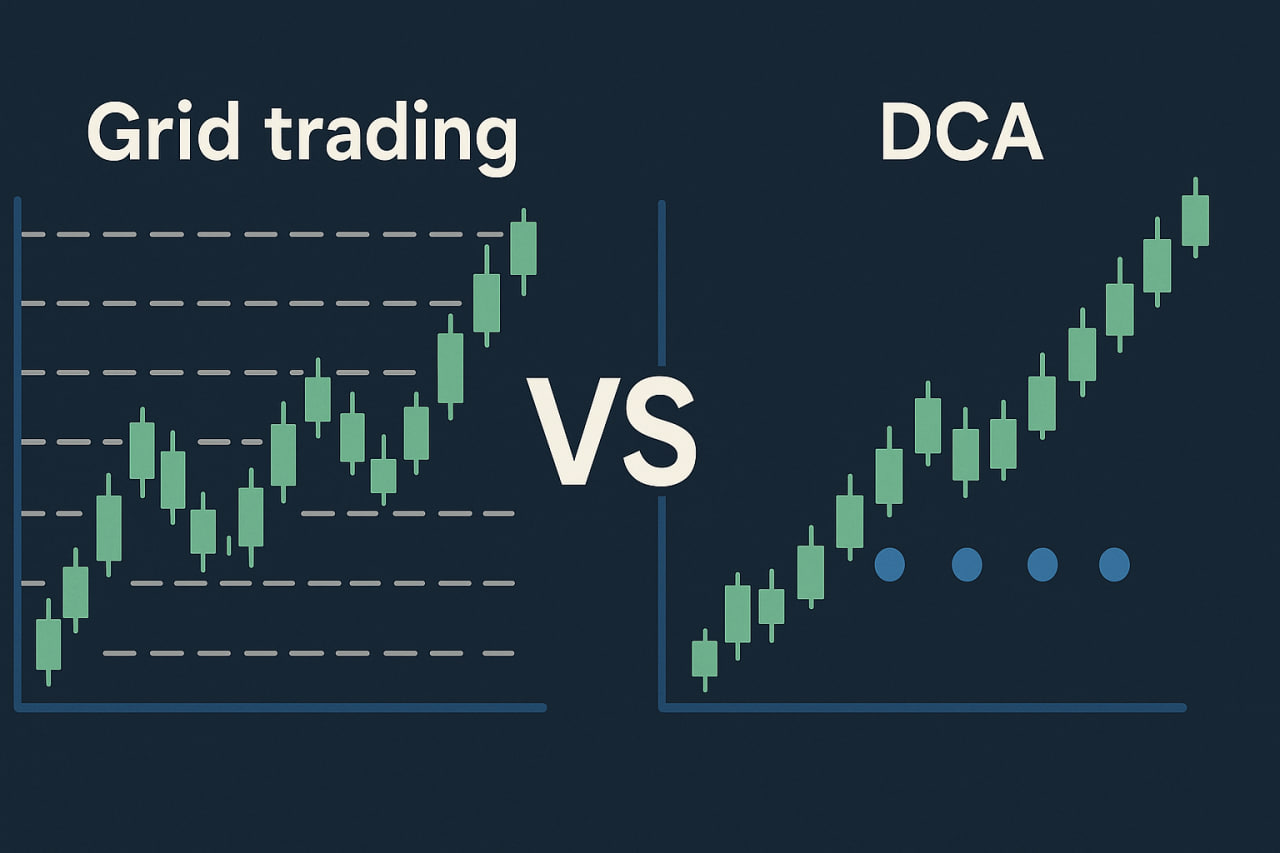
Profitability and Resilience
In a bear market, the outcomes of these strategies differ:
- The profitability of grid trading depends on the amplitude of fluctuations: in a sideways market, the bot can generate income, but during sustained upward or downward trends, losses may accumulate.
- DCA operates differently in a bear market: the investor systematically lowers the average entry price, which can yield benefits only if the market recovers in the future.
Risk Management
Grid trading requires constant monitoring of the price range and sufficient capital to manage risk effectively. Errors in setup can lead to significant losses. DCA, on the other hand, minimises the risks of poor timing but requires patience and readiness for long-term drawdowns.
Suitability for Different Types of Investors
The following table helps compare these strategies:
| Criterion | Grid Trading | DCA |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Profit from volatility | Long-term accumulation |
| Time Horizon | Short- to medium-term | Long-term |
| Risks | High during prolonged trendless markets | Moderate during extended declines |
| Tool | Grid trading bot | Bot for regular purchases |
| Suitable for | Active traders | Medium- and long-term investors |
Practical Recommendations

The choice of strategy depends on the investor’s goals and psychology.
If short-term dynamics are important and there is experience in configuring trading bots, grid trading can be highly effective. For those building a long-term portfolio and willing to wait for market recovery, DCA remains a reliable tool.
Combining Strategies
Some investors combine these approaches to offset the weaknesses of each:
-
Allocating part of the capital to grid trading to profit from price fluctuations
-
Using DCA for long-term asset accumulation
-
Dividing the portfolio into “active” and “investment” portions
-
Configuring different bots for various market scenarios
A hybrid approach helps mitigate the impact of market volatility and maintain a balance between risk and return.
Conclusion
When comparing grid trading and the DCA strategy, it becomes clear that each reflects a different approach to engaging with the market: one seeks to capitalise on short-term movements, while the other relies on time and patience.
Thus, the key is not choosing the “right” strategy but understanding one’s own goals and risk tolerance. A thoughtful evaluation of these factors allows investors to leverage market cycles to their advantage, generating profits in any market environment.