How to Calculate Position Size Before Opening a Trade

Contents
- Introduction
- Why is the correct calculation necessary for successful trading
- Overview of the basic principles of risk management in trading
- What is the position size?
- Market volatility
- Methods for calculating the position size
- An example of calculating the position size
- Mistakes in calculating the position size
- Tools and calculators for calculating position size
- Conclusion
Introduction
Calculating the position size is one key aspect of successful trading in financial markets, including cryptocurrency. Incorrect calculation can lead to excessive losses, even if you have good trading strategies. Therefore, it is important to understand how to correctly determine how much money to invest in each transaction to minimise risks and maintain long-term stability.
Why is the correct calculation necessary for successful trading
The correct position size calculation helps control risks and avoid significant losses. It allows the trader to determine how much money should be invested in a particular trade, considering the total capital and the acceptable level of risk. Losing one trade can significantly affect your capital if you invest too much. On the other hand, positions that are too small can limit profits if the trade is booming. A perfectly balanced position size helps traders use their capital effectively, minimising risks and increasing the chances of successful trades.

Overview of the basic principles of risk management in trading
- The 1-2% rule is one of the simplest and most effective risk management methods. This means that you risk no more than 1-2% of the total capital in one transaction. For example, if your capital is $1,000, the maximum risk per trade is $10-20. This allows you to minimize losses in the event of a failed trade, while maintaining growth opportunities.
- Stop losses —Setting stop losses at each risk level is important. These are automatic orders that close a trade when a certain price is reached, limiting possible losses. A stop loss helps you adhere to established risk boundaries, even if you don’t have time to react to market changes immediately.
- Diversification — it is not worth investing all your funds in one transaction or one cryptocurrency. The division of capital between several positions reduces the overall risk of losses. It also allows you to exploit opportunities in various markets and assets.
- Using margin — If you plan to use margin trading, consider the increased risks. Margin increases potential profits and possible losses, so the position size must be carefully calculated to avoid account liquidation.
Calculating position size is an essential skill for capital protection and the key to long-term success in trading. Understanding risk management principles and the ability to allocate funds between trades properly will help you avoid significant losses and trade effectively, even if you are just starting.
What is the position size?
The position size is the amount of funds or units of an asset a trader decides to invest in one particular trade. This definition depends on the total capital, the level of risk that the trader is willing to accept, and market conditions. The size of the position helps the trader control his financial risks, and determines how much profit or loss he can receive from the transaction in the event of a change in the asset price.
The importance of choosing the right position size
Choosing the right position size is crucial for successful trading. If the position size is too large, even small price fluctuations can lead to significant losses, which jeopardise the entire trading capital. On the other hand, if the position size is too small, it can limit the potential profit, even if the trade is booming.
- Risk minimisation: By determining the position size, the trader can set stop losses to limit possible losses. The risk per trade must be only a tiny part of the total capital (for example, 1-2%). This avoids significant losses that can destroy the entire deposit.
- Profit maximisation: The correct position size calculation helps the trader use his capital effectively. By increasing the position size moderately with proper risk management, you can increase the profits from successful trades without incurring excessive risks.
Position size is a balance between risk and possible profit. It is one of the most important aspects of determining one’s ability to survive and thrive in the financial markets.
The main factors influencing the calculation of the position size
The correct position size calculation depends on several factors that help a trader determine how much money to invest in a particular trade to balance risk and potential profit.
The level of risk (how much capital are you willing to lose)
This factor includes determining how much you will lose if you fail. Many traders rule that the risk per trade should not exceed 1-2% of the total capital. For example, if your deposit is $1,000, the maximum risk per trade is $10-20. This level of risk helps limit losses and save capital for further transactions, even if several transactions are unprofitable.
Stop loss (the distance from the current price to the stop loss level)
A stop loss is an order that automatically closes a trade if the price of an asset reaches a certain level to limit losses. The distance from the current price to the stop loss level affects the position size: the further the stop loss is from the current price, the smaller the position size can be taken to stay within the acceptable risk. For example, if the stop loss is set at 10% below the current price, and you are willing to risk 2% of the capital, the position size should be calculated so that the losses from this transaction do not exceed 2%.
The size of the deposit and its share, which the trader is willing to allocate for one transaction
The size of the deposit and the choice of the share of capital that the trader is willing to allocate for one trade directly affect the size of the position. For example, if you have $500 in your account and you are ready to allocate 5% of the deposit for one transaction, the maximum position size will be $25. This amount must match your risks and strategy.
Market volatility
Volatility is the degree to which prices change in a market. The higher the volatility, the more likely the price will fluctuate widely, which can lead to unexpected losses. In high volatility conditions, traders usually reduce their position size to reduce risks, as large price fluctuations can lead to significant losses. In conditions of low volatility, it is possible to increase the position size, as the price will move more smoothly.
Thus, calculating the position size requires considering these factors to balance risks and profits. Properly using these elements helps traders manage their capital effectively and avoid excessive risks.
Methods for calculating the position size
The correct position size calculation helps traders effectively manage risks and optimise their chances of success in the market. Several popular calculation methods exist, each focusing on different money and risk management approaches.
Fixed percentage method
This method involves investing a fixed percentage of the total deposit in each trade. For example, if you decide to risk 2% of your capital on each trade, you need to calculate the monetary value of this amount.

Thus, you are ready to lose $20 in case of failure.
Now, it is necessary to calculate the position size while considering the stop loss.
For example, if the stop loss is 10% of the current asset price, then the position size will be calculated as:
$20 (maximum losses) / 10% (distance to stop loss) = $200.
That is, to risk $20, you need to open a position worth $200.
The method of calculation through the risk per transaction
This method allows you to calculate the position size more accurately, considering the specific risk level per trade and stop loss. You determine how much you will lose in percentage or monetary terms, and then use the stop loss information to calculate the number of lots or position size.

To calculate the position size, use the formula:
Position size = Risk per trade / Stop Loss percentage
Position size = 10/5%×100 = 10/5 = 2
Thus, you can buy two units of an asset (for example, two coins of cryptocurrency) without risk, more than $10 in case of a stop loss.
The risk-reward ratio (R/R) method
The Risk/Reward (R/R) calculation method involves choosing the position size based on how much profit you expect to receive compared to possible losses. This helps the trader decide how profitable a trade is in terms of the ratio of risk and potential profit.
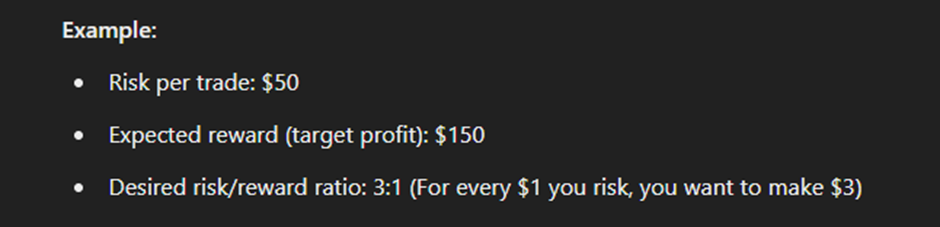
To determine the position size based on R/R, you must calculate how much transaction volume corresponds to this ratio. If your risk per trade is $50 and the R/R ratio is 3:1, your expected profit will be $150. This allows you to choose positions that meet your profit and loss expectations without risking more than a certain percentage of capital.
An example of calculating the position size
Let’s calculate the position size step-by-step using specific figures and various trading instruments (stocks, currencies, futures, etc.).
Calculating the position size for stocks
Let’s say you want to trade stocks and you need to determine the position size that matches your risk level.
Example:
- Total capital: $10,000
- Percentage of risk per trade: 2% (0.02)
- Share price: $50
- Distance to stop loss: 5% (0.05) of the current price
Step 1: Calculate the amount you are willing to lose on the deal.
Risk per trade = 10,000 × 0.02 = 200
You are willing to risk $200 on this trade.
Step 2: Calculate the stop loss price.
The share price is $50, the stop loss is set 5% lower than the current price:
Risk per share = 50 × 0.05 = 2.5
Thus, the stop loss will be set at $47.50 (50 - 2.5).
Step 3: Calculate the number of shares to buy.
Now you can calculate the position size by dividing the risk per trade by the amount of risk per share (the distance to the stop loss):
Position size = Risk per trade/Risk per share = 200/2.5 = 80
So you can buy 80 stocks, risking $200 with a stop loss at $47.50.
Calculating the position size for a currency pair (Forex)
Let’s say you want to trade the EUR/USD currency pair.
Example:
- Total capital: $5,000
- Percentage of risk per trade: 1% (0.01)
- Stop loss: 50 pips (0.0050)
- EUR/USD currency pair: the current exchange rate is 1.2000
- Contract size: 1 standard lot = 100,000 units of the base currency (Euro)
Step 1: Calculate the amount you are willing to lose on the deal.
Risk per trade = 5,000 × 0.01 = 50
You’re willing to risk $50 on a trade.
Step 2: Calculate the cost of 1 pips.
For the EUR/USD currency pair, 1 pips for a standard lot is $10. This means a 1 pips change in the exchange rate will affect your position by $10.
Step 3: Calculate the number of lots to buy.
Now, to calculate the position size, you need to consider that you are risking $50 and want to set a stop loss of 50 pips. Thus, each pip will cost $10.
Position Size = Risk per trade/Risk per 1 pips
Position size=50/10×50 = 50/500 = 0.1
Thus, you need to open a 0.1 lot position.
Calculating the position size for futures contracts
You trade oil futures (for example, a WTI contract).
Example:
- Total capital: $10,000
- Percentage of risk per trade: 2% (0.02)
- Futures contract price: $70 per barrel
- Stop loss: $2 (distance from current price)
Step 1: Calculate the amount you are willing to lose on the deal.
Risk per trade = 10,000 × 0.02 = 200
You are willing to risk $200 on a trade.
Step 2: Calculate the risk for one contract.
The risk per futures contract is the difference between the entry price and the stop loss price:
The risk per contract = 2
Step 3: Calculate the number of contracts to buy.
Now you can calculate the number of contracts you need to buy, not to risk more than $200:
Position size=Transaction risk/Contract risk = 200/2=100
So you can buy 100 oil contracts, risking $200 with a stop loss at $68.
Each type of trading instrument requires an individual approach to calculating the position size based on the characteristics of the asset, risks, and available capital. Correct position calculation helps traders minimise possible losses and effectively manage risks.
Mistakes in calculating the position size
Correct position size calculation is an essential aspect of successful trading. Here are the main mistakes that can lead to losses.
Overkill with the position size (too much risk)
Traders sometimes risk too much capital, which increases the likelihood of significant losses. For example, if the risk per transaction is 50% of the deposit, then if the transaction fails, you can lose half of your capital.
Underestimating the size of the position (too little risk)
When traders risk too little, they may miss out on profitable opportunities. For example, if the risk of a trade is only 0.1%, even successful transactions will not bring significant income.
Ignoring market volatility
Some traders do not consider an asset’s volatility when calculating a position. This leads to frequent stop-loss triggers, especially when trading volatile assets such as cryptocurrencies or stocks.
Recommendation: Consider the asset’s volatility and set a wider stop loss for volatile markets to avoid unnecessary losses due to normal market fluctuations.
Mistakes in calculating the position size can seriously affect trading results. Balanced risk management, accounting for volatility, and adequate position size will help you manage your capital more effectively and minimise losses.
Tools and calculators for calculating position size
Traders can use various online tools and calculators to calculate their position size accurately. They help automatically consider all transaction parameters, minimising calculation errors.
Overview of available online tools and calculators
There are many calculators and tools available for traders that will help you calculate your position size correctly:
-
Position Size Calculator
These calculators allow you to calculate the position size based on the selected risk level and stop loss. The user enters the deposit amount, risk percentage, stop loss, and asset price, and the calculator automatically calculates the position size.
-
Profit and Loss Calculator
This tool calculates how much you can earn or lose on a trade, considering the initial price, stop loss and take profit prices, and the position’s volume.
-
Calculators for currency pairs (Forex Position Size Calculator)
Special calculators for the Forex market that consider the specifics of currency pairs, their volatility, lots and coefficients to accurately calculate the position size.
-
Futures Calculators
These tools are designed for futures traders and consider parameters such as contract size, market price, and stop loss distance to help them calculate a position correctly.
Advantages of automatic calculations
-
Accuracy
Automatic calculators consider all transaction parameters and minimise the possibility of errors that may occur during manual calculations.
-
Saving time
These tools speed up the calculation process, allowing traders to focus on other essential aspects of trading, such as market analysis.
-
Stress reduction and trade facilitation
When calculations are performed automatically, traders worry less about possible errors and can confidently decide the size of positions.
-
Flexibility
Calculators offer settings for different types of assets, including stocks, currencies, cryptocurrencies, and futures, allowing traders to use them for different markets.
Using online tools and calculators to calculate position size helps avoid mistakes, speed up the process, and improve trading decisions. These critical tools make the trading process more manageable and less stressful.
Conclusion
Correct position size calculation is a key part of successful trading, which helps to control risks and ensure stable results. Considering the level of risk, stop loss, market volatility, and capital, traders can accurately determine the optimal position size, minimising losses and maximising potential profits. Using online calculators and automated tools simplifies this process, increasing the accuracy of calculations and saving time. Considering these principles, traders can make more informed and confident decisions when opening trades