How to Use Liquid Staking Tokens (LST) to Increase Yield

Contents
- Introduction
- Principles of operation of liquid staking tokens
- The main ways to increase profitability using LST
- Adding LST to Liquidity Pools on DEXs (Decentralized Exchanges)
- Using LST to Generate Additional Tokens
- Providing LST in Lending Protocols
- Using LST as Collateral
- Using Platforms for Compound Interest
- Risks and Limitations of Using LST
- Recommendations for Choosing a Strategy
- Examples of LST Utilization Strategies
- The Future of Liquid Staking Tokens
- Restaking
- Integration with DeFi Protocols
- Multichain Staking
- Automated Yield Strategies
- Conclusion
Introduction
Liquid staking allows users to participate in staking without having to freeze their assets.
What are Liquid Staking Tokens (LST)
Liquid staking tokens (LST) are collateral assets in the blockchain used in Proof-of-Stake (PoS) systems. In traditional staking, there is a lockdown period during which tokens cannot be accessed or traded. LST tokens solve this problem and allow users to freely use them in other financial transactions while retaining the right to staking rewards.
Example: Let’s say you have 10 ETH and want to send it to staking to generate income. In regular staking, these coins are blocked, and you cannot use them.
But if you stake them through an LST platform, for example, Lido, in return for your 10 ETH, you get 10 stETH (liquid staking tokens of Lido), which can be used in the same way as regular ETH: for example, to trade or use in DeFi protocols. At the same time, your 10 ETH continues to earn you a reward for staking.
Why are LSTs popular in DeFi, and how do they help increase profitability
The popularity of LST in the field of decentralized finance (DeFi) is due to several factors:
- Increased liquidity: Unlike traditional stacking, where assets are frozen for a certain period, LST allows users to maintain access to their funds.
- Additional sources of income: Thanks to LST’s liquidity, users can simultaneously receive staking rewards and use their tokens in other DeFi protocols.
Principles of operation of liquid staking tokens
The basics of liquid staking
Consider the process of liquid staking:
-
Deposit: The user deposits his tokens into the smart contract of the liquid staking platform.
-
Receiving LST: In return, the user gets liquid staking tokens (LST) representing his share of the staked assets.
-
Using LST: These LSTs can be used in various decentralized financial (DeFi) applications such as lending, trading, or participating in liquidity pools, allowing for additional income.
The LST is released and burned automatically. Protocols can issue various derivative assets, such as Rebase, Reward, and Rebase + Reward.
- Rebase: The number of tokens varies depending on the staking awards (wETH).
- Reward: The price of the token increases due to the accrued rewards, but it is fixed only during the reverse exchange (yETH).
- Rebase + Reward is a hybrid option that allows you to convert one type to another (stETH ↔ wstETH).
Examples of popular liquid staking platforms

Many platforms provide liquid stacking services. Below are some of them:
Lido
Lido is a liquid staking platform that allows users to stake their tokens and receive derivative assets. These derivative tokens can be freely used in DeFi applications.
Rocket Pool
Rocket Pool is a decentralized Ethereum staking protocol that allows users to place at least 0.01 ETH in staking to receive rewards. Users receive rETH tokens representing their share of the acquired assets, which can be used in other DeFi applications.
mEth Protocol
mEth Protocol is a liquid staking platform offering users the opportunity to stake ETH. In return for the frozen assets, users receive mETH, which can be used in DeFi protocols, or immediately sent to restaking, which is offered inside the platform.
Advantages of using LST
The use of liquid stacking tokens provides the following advantages:
-
Maintaining liquidity: Participating in stacking without having to freeze your assets.
-
Additional Profitability: Using LST in DeFi protocols to generate extra profits on top of staking rewards.
-
Capital efficiency: Extracting more profit from the same amount of funds due to the release of liquidity.
The main ways to increase profitability using LST
Using LST in liquidity pools
Adding LST to Liquidity Pools on DEXs (Decentralized Exchanges)
Providing LST tokens to liquidity pools on platforms such as Uniswap, Curve, and Balancer enables users to earn income through transaction fees generated from token swaps within the pool.
Example: Imagine you hold stETH tokens (a liquid staking token from Lido). You add them to the stETH/ETH liquidity pool on Curve Finance. Whenever other users swap stETH for ETH or vice versa, you receive a portion of the transaction fees as a reward.
Yield Farming
Using LST to Generate Additional Tokens
Yield farming is a decentralized finance (DeFi) strategy that provides liquidity to various DeFi protocols in exchange for rewards, typically paid in additional tokens.
Example: A user stakes ETH on the Lido platform and receives stETH at a 1:1 ratio. They then deposit stETH and ETH into a liquidity pool on Curve, receiving LP tokens in return. These LP tokens can be staked on Convex Finance to earn additional rewards like CVX and CRV tokens. This way, the user simultaneously benefits from staking rewards on Lido and additional incentives from liquidity provision and yield farming.
Lending and Borrowing
Providing LST in Lending Protocols
Platforms like Aave and Compound allow users to earn interest on liquid staking tokens (LST) by lending them to others. This operates similarly to traditional bank deposits, where depositors earn interest on their funds, but in this case, the assets are utilized within the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
If you hold LST tokens (e.g., stETH or rETH), you can deposit them into a lending protocol. These tokens will then be used to provide loans to other users, generating passive income for you through interest.
Example:
- You deposit 10 stETH into Aave.
- The protocol uses these tokens to issue loans.
- In return, you earn a 3% annual yield.
- After one year, your balance grows to 10.3 stETH, which you can withdraw anytime.
Using LST as Collateral
Instead of simply holding your LST tokens, you can use them as collateral to take out loans in stablecoins (e.g., USDT or DAI). This works similarly to a secured loan at a bank: you pledge a valuable asset and receive funds in return, which can be used for other investments.
Example:
- You deposit 10 stETH as collateral on the Compound.
- The protocol allows you to borrow DAI equivalent to 7 ETH.
- You use the borrowed DAI to purchase additional assets.
- Later, you repay the loan and regain full access to your 10 stETH.
This approach allows users to leverage their LST holdings while maintaining exposure to their staked assets.
Automated Reinvestment Strategies

Using Platforms for Compound Interest
Platforms such as Yearn Finance and Beefy enable users to automatically reinvest their earnings, increasing overall returns through compound interest without requiring constant monitoring.
Example: A user deposits their crypto assets into Yearn Finance. The platform automatically reinvests the earned interest, increasing the total investment amount. Through regular reinvestment, the user benefits from the power of compound interest, resulting in higher long-term returns.
Risks and Limitations of Using LST
Market Risks: Price Volatility of LST on Secondary Markets
Liquid staking tokens (LST) can fluctuate significantly in secondary markets. Changes in supply and demand or broader market conditions may drive these price swings. As a result, even if the underlying staked assets continue to generate rewards, the market price of LST may decline, leading to potential losses for holders.
Risks of Liquid Staking Platforms: Smart Contract Security
Liquid staking platforms rely on smart contracts to automate staking processes and issue derivative tokens. However, vulnerabilities or coding errors in these smart contracts could be exploited by malicious actors, potentially leading to the loss of user funds.
Potential Loss of Earnings Due to High Fees and Intense Competition in DeFi
In the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem, transaction fees can be high, especially during periods of network congestion. Additionally, intense competition among DeFi protocols can reduce the profitability of liquidity provision or yield farming. As a result, the overall returns from using LST may be lower than expected, and in some cases, transaction fees may outweigh the rewards earned.
Recommendations for Choosing a Strategy
Before implementing liquid staking strategies, it is essential to define your financial goals, assess your risk tolerance, and select a reliable platform with a strong reputation

Assessing Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
Defining Financial Goals:
- Short-term goals: Examples include saving for upcoming expenses.
- Long-term goals: Such as achieving financial independence or building a retirement fund. Having a clear understanding of your objectives helps you select appropriate investment strategies.
Evaluating Risk Tolerance:
- High risk: Potential for significant profits, but with high volatility and a greater chance of losses.
- Low risk: Greater capital stability but with more moderate returns.
Assessing your personal risk tolerance and considering your financial situation before making investment decisions is essential.
Tips for Choosing Platforms and Protocols
Selection Criteria:
- Reliability and security: Prefer platforms with a proven track record and secure smart contracts.
- Transparency: Open-source code and accessible information about the development team.
- Community and support: An active user community and responsive customer support.
Before committing significant funds, research available platforms, their functionality, and user feedback. It is recommended to start with small amounts to evaluate the platform’s performance and usability.
Verifying the Reputation and Security of DeFi Protocols
Security Audit:
- Audit verification: Ensure the protocol has undergone an independent security audit.
- Audit results: Review reports and recommendations from security auditors.
Community Reputation:
- Reviews and ratings: Check user and expert opinions on the protocol.
- Incident History: Investigate past security issues and how they were resolved.
Development Activity:
- Regular updates: Frequent updates indicate ongoing support and protocol development.
- Community engagement: An active community helps identify and address potential issues.
Examples of LST Utilization Strategies

Staking Stablecoins
A user leverages LST as collateral to borrow stablecoins (DAI, USDC, USDT) and then stakes them to generate additional yield.
Example: Aave + Spark Protocol:
- The user deposits stETH into Aave and borrows DAI at a 2-3% interest rate.
- The borrowed DAI is then staked in Spark Protocol, which offers a 5-8% APY on stablecoins.
- Net profit: The difference between the borrowing cost and the staking yield (2-5% APY).
Lending LST on DeFi Platforms
Users can supply their LST to lending protocols like Aave or Compound to earn passive interest.
Example:
- Aave: Depositing stETH earns 3-5% APY.
- Compound: Offers similar rates for rETH, stETH, and other LST.
Providing Liquidity with LST
Users can add LST to Uniswap, Curve, or Balancer liquidity pools and earn trading fees.
Example:
- Curve: The stETH/ETH liquidity pool can generate 10-20% APY (fees + CRV token rewards).
Yield Farming with LST
LST can be utilized in Yield Farming strategies to earn additional rewards.
Example:
- Yearn Finance: Depositing stETH enables automatic compounding, increasing yield to 5-15% APY.
- Beefy Finance: Similarly, it reinvests earnings automatically to maximize returns.
Comparative strategy table
| Strategy | Yield (APY) | Risks |
| Stablecoin Staking | 2-5% | Changes in interest rates |
| Lending LST on DeFi Platforms | 3-5% | Smart contracts, bid changes |
| Providing Liquidity with LST | 10-20% | Impermanent loss |
| Yield Farming with LST | 5-15% | Smart contracts, volatility |
The Future of Liquid Staking Tokens

Trends and Innovations in Liquid Staking
In recent years, liquid staking has evolved with new trends and innovations, making the staking process even more flexible and profitable.
Here are some key developments:
Restaking
Restaking allows staked crypto assets to be reused to secure blockchain protocols, enhancing capital efficiency and generating additional yield.
Integration with DeFi Protocols
Liquid staking tokens (LSTs) are widely used across various DeFi protocols, including lending, borrowing, and liquidity pools, expanding their utility.
Multichain Staking
Many platforms now support liquid staking across multiple blockchains simultaneously. This enables users to diversify their investments and earn rewards from different networks.
Automated Yield Strategies
Integrating liquid staking with automated yield optimization strategies allows users to maximize returns by dynamically reallocating assets.
Impact on the DeFi Ecosystem and Users
Liquid staking has profoundly impacted the DeFi ecosystem, unlocking new user opportunities.
Capital use has become more efficient, which attracts even more participants. In addition, the integration of liquid stacking with credit protocols, liquidity pools, and other DeFi services has created new financial instruments and made the ecosystem more dynamic.
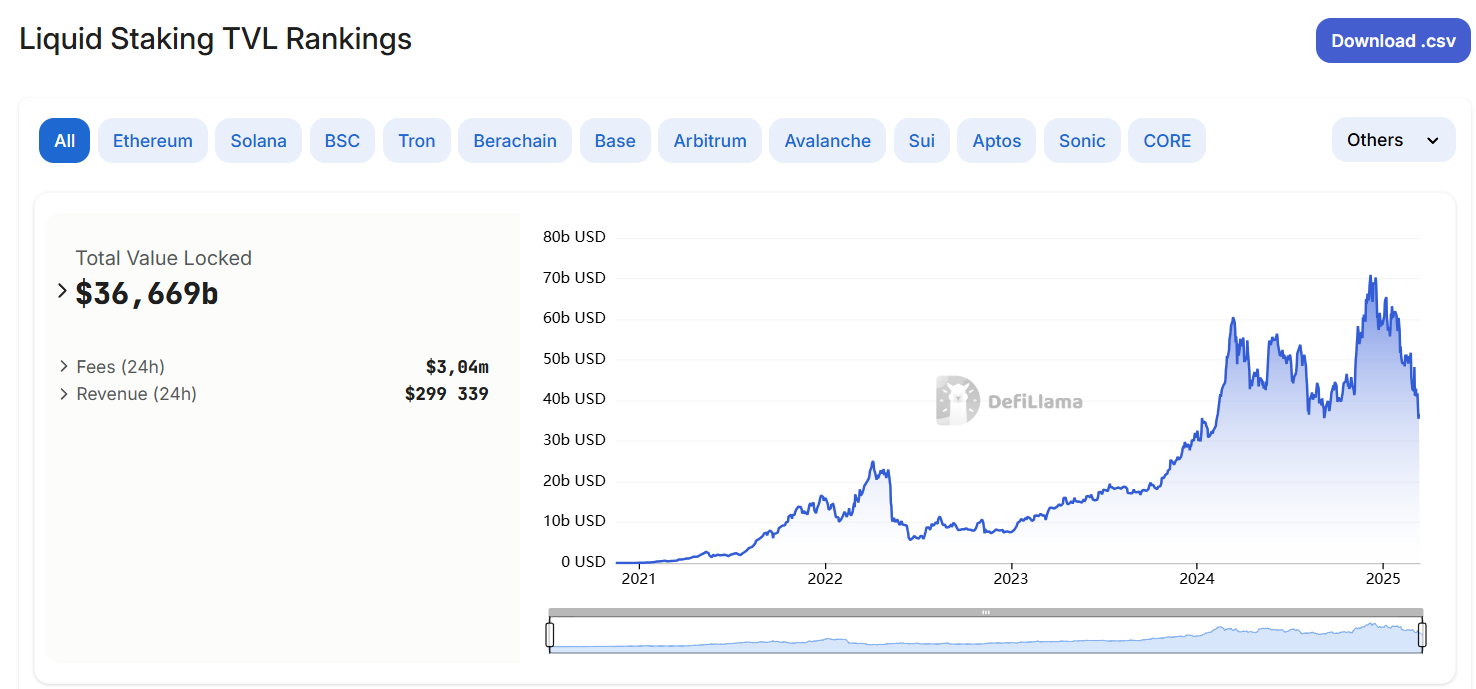
The popularity of liquid stacking is growing due to the emergence of new tools and the convenience offered to users. At its peak, the volume of blocked funds in liquid staking protocols reached $70 billion. Currently, TVL amounts to more than $36 billion, which accounts for about half of the total funds of the entire DeFi segment.
Conclusion
Liquid staking and LST tokens open new opportunities for investors. Users are drawn to the flexibility—the ability to create personalized strategies based on their preferences, risk management, and deposit size. However, opportunities come with risks: LST price volatility, smart contract vulnerabilities, and potential losses due to high fees or competition.
The future of liquid staking looks promising, with new protocols, enhanced security mechanisms, and integration with a broader range of DeFi products. As the technology evolves, liquid staking may become an integral part of the cryptocurrency market and the entire financial industry.
Nevertheless, before investing, it is crucial to carefully analyze platforms, assess risk levels, and choose strategies that align with your financial goals. Only a well-informed approach will allow you to fully leverage the potential of liquid staking and generate stable long-term returns.