What are cryptocurrency ETFs and how do they work?

In recent years, cryptocurrencies have been rapidly gaining popularity as a new investment asset class. However, direct ownership of cryptocurrencies is fraught with a number of challenges, including high volatility, the need to understand technical aspects and safe storage issues. Against this background, cryptocurrency ETFs – exchange-traded investment funds that allow indirect investment in cryptocurrencies – are becoming increasingly relevant.
Contents
- What is an ETF?
- Cryptocurrency ETFs
- How do cryptocurrency ETFs work?
- Advantages of cryptocurrency ETFs
- Risks and drawbacks of cryptocurrency ETFs
- Cryptocurrency ETFs in the world
- How to start investing in cryptocurrency ETFs?
- Conclusion
What is an ETF?
An ETF (Exchange Traded Fund) is an exchange-traded investment fund whose units are freely traded on an exchange like stocks. Each ETF tracks the performance of a specific underlying asset, such as a stock index, economic sector, commodity or basket of assets.
The way ETFs work is as follows: the fund acquires underlying assets (stocks, bonds, futures, etc.) and issues units against them. The value of an ETF unit is linked to the value of its assets and changes during the trading day following changes in the price of the underlying asset. Investors can buy and sell ETF units on the exchange in the same way as ordinary shares.
ETFs give investors the opportunity to effectively diversify their investments. By purchasing just one unit, an investor is essentially buying an entire portfolio of the assets underlying that ETF. This allows even small investors to spread their funds across a wide range of instruments, sectors and asset classes, which reduces risk and increases portfolio stability.
Examples of popular traditional ETFs:
- SPDR S&P 500 (SPY) – The oldest and largest ETF tracking the S&P 500 Index.
- Invesco QQQ (QQQ) – ETF on the NASDAQ-100 index of high-tech companies.
- SPDR Gold Trust (GLD) – An ETF that holds physical gold to track its price.
- iShares MSCI Emerging Markets (EEM) – ETF on a basket of emerging markets stocks.
- Vanguard Total Bond Market (BND) – ETF that provides broad exposure to the U.S. investment-grade bond market.
These and other ETFs are popular with investors due to low fees, ease of investing and good portfolio diversification.
Cryptocurrency ETFs
Cryptocurrency ETFs are exchange-traded investment funds that track the price performance of one or more cryptocurrencies. They are traded on traditional exchanges and allow investors to access the growth of the cryptocurrency market without having to buy and hold cryptocurrencies directly.
Key differences between cryptocurrency ETFs and traditional ETFs:
- Underlying asset. Crypto-ETFs are based on cryptocurrencies or cryptocurrency derivatives (futures, options) rather than stocks, bonds or exchange-traded commodities.
- Volatility. Cryptocurrencies are characterized by much higher volatility compared to traditional assets, which is reflected in the dynamics of crypto-ETFs.
- Regulation. Cryptocurrency ETFs face stricter regulation and restrictions from financial regulators due to the specific nature of the underlying asset.
Crypto-ETFs can include either one or multiple cryptocurrencies for greater diversification.
By structure, there are two main types of cryptocurrency ETFs:
- Physical ETFs are funds that directly own cryptocurrencies. They buy coins and store them in their cryptocurrency wallets, providing physical ownership of the asset.
- Futures ETFs – funds that invest in cryptocurrency futures instead of directly buying cryptocurrencies. This structure eliminates the need for the fund to hold cryptocurrencies and simplifies regulatory compliance.
Both types of crypto-ETFs have their advantages and disadvantages and can be used by investors depending on investment preferences and risk tolerance.

How do cryptocurrency ETFs work?
The mechanism of crypto-ETF value formation depends on its structure. For physical ETFs, the value of a unit is determined by the price of cryptocurrencies included in the fund. As the quotes of cryptocurrencies on the spot market change, the price of the ETF also changes. For futures ETFs, the price of a unit depends on the dynamics of cryptocurrency futures, which is usually close to the spot market prices, but may deviate due to the peculiarities of the derivatives market.
Exchanges and intermediaries play a key role in cryptocurrency ETFs:
- Cryptocurrency exchanges and OTC platforms (for physical ETFs) – used by the fund to buy and sell cryptocurrencies forming the ETF portfolio.
- Traditional exchanges – platforms where cryptocurrency ETF units are listed and traded. These are exchanges that trade stocks, futures and other traditional instruments.
- Market makers and authorized participants – intermediaries that provide liquidity of crypto-ETFs on the exchange and maintain the correspondence between the unit price and the value of the underlying assets.
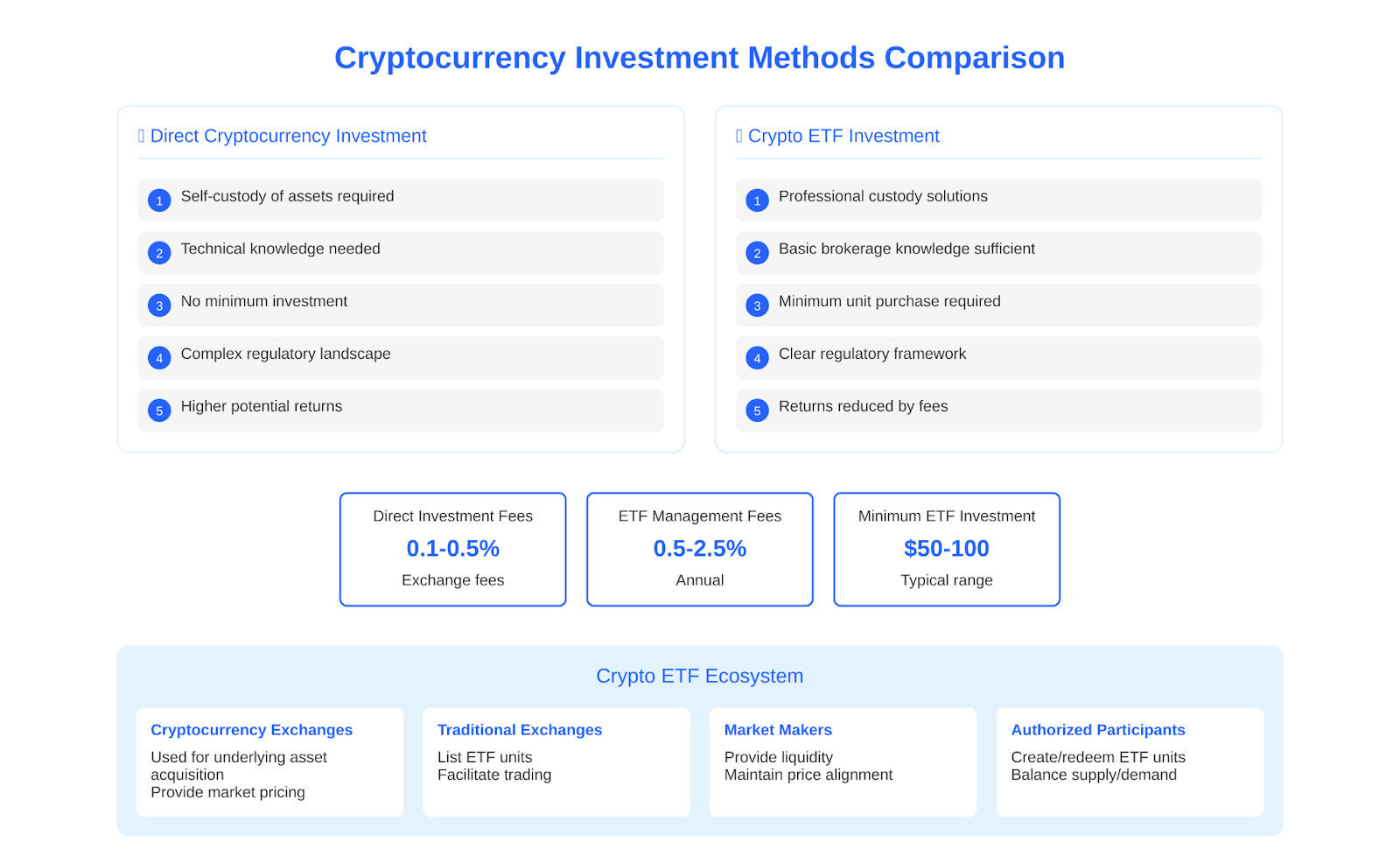
Owning cryptocurrencies directly and investing through crypto-ETFs have some key differences:
- Asset Storage. With a direct purchase, the investor is responsible for safe custody of the cryptocurrencies themselves. When investing through an ETF, the investor owns units of the fund, and the ETF itself is responsible for storing the cryptocurrencies.
- Required knowledge and skills. To buy and sell cryptocurrencies independently, an investor needs to understand the workings of cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets. In the case of crypto-ETFs, it is enough to know how to work with a traditional brokerage account.
- Minimum investment amount. Direct investment in cryptocurrencies is possible for any amount. Investing through ETFs usually requires capital sufficient to purchase at least one unit.
- Regulation and taxation. Investing through cryptocurrency ETFs is more transparent and understandable from a regulatory and tax perspective, as ETFs are regulated investment products.
- Potential returns. Direct ownership of cryptocurrencies offers the potential for greater returns if prices rise, while in the case of ETFs, some of the returns are eaten up by fund fees.
Thus, crypto-ETFs provide a simpler and more straightforward way of investing in cryptocurrencies, but have their own features and limitations compared to the direct purchase of digital assets.
Advantages of cryptocurrency ETFs
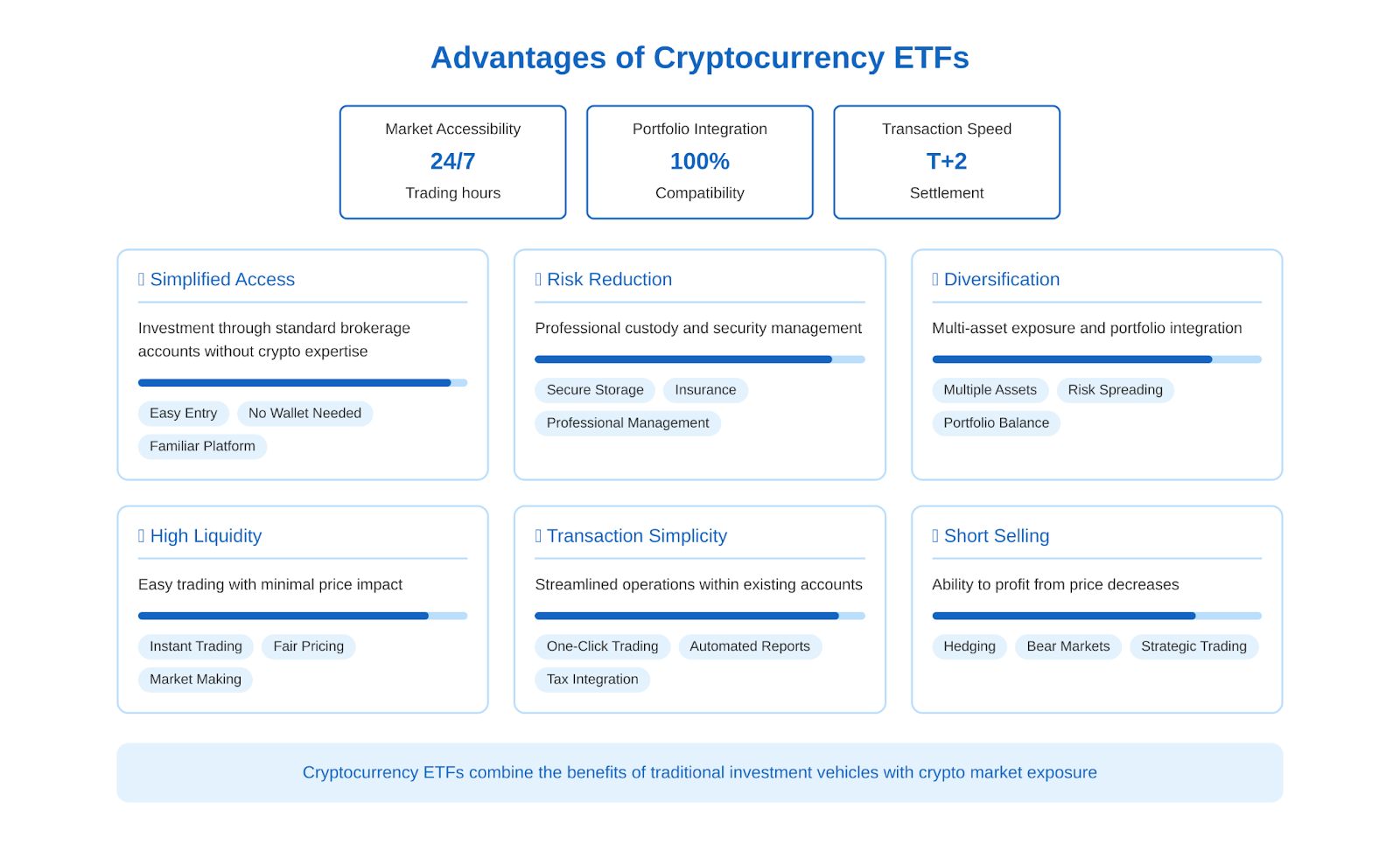
Cryptocurrency ETFs offer investors many advantages over investing directly in digital assets:
- Simplified access to cryptocurrencies. Crypto-ETFs allow you to invest in cryptocurrencies without having to learn the specifics of cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets. You simply need to buy ETF units through your usual brokerage account. This makes the cryptocurrency market accessible to a wide range of investors, including institutional and conservative investors.
- Reducing specific risks. By investing through an ETF, an investor shifts the risks associated with cryptocurrency custody and security to a professional fund management team. This reduces the likelihood of losing crypto assets due to technical errors or hacker attacks.
- Diversification. Cryptocurrency ETFs that include multiple digital assets provide diversification of investments within the cryptocurrency class. This helps reduce the risks associated with the volatility of individual coins. In addition, adding cryptocurrencies through ETFs to a traditional investment portfolio contributes to its overall diversification.
- High liquidity. Cryptocurrency ETF units are freely traded on exchanges and can be bought or sold at any point in the trading session at close to a fair price. An investor does not need to select a counterparty for the transaction or worry about price slippage, as it happens when trading on cryptocurrency exchanges.
- Simplicity of transactions. All operations with cryptocurrency ETFs (buying, selling, profit accounting) take place within the investor’s standard brokerage account. This simplifies the management of the investment portfolio, in which cryptocurrency
- Possibility of short selling. Unlike the spot cryptocurrency market, on the ETF exchange it is possible to open short positions on cryptocurrency funds and earn on the fall in the price of the underlying digital assets. This expands investors’ ability to manage their portfolio.
These advantages make cryptocurrency ETFs an attractive tool for both investors new to the cryptocurrency market and experienced investors looking to simplify the management of their digital assets.
Risks and drawbacks of cryptocurrency ETFs
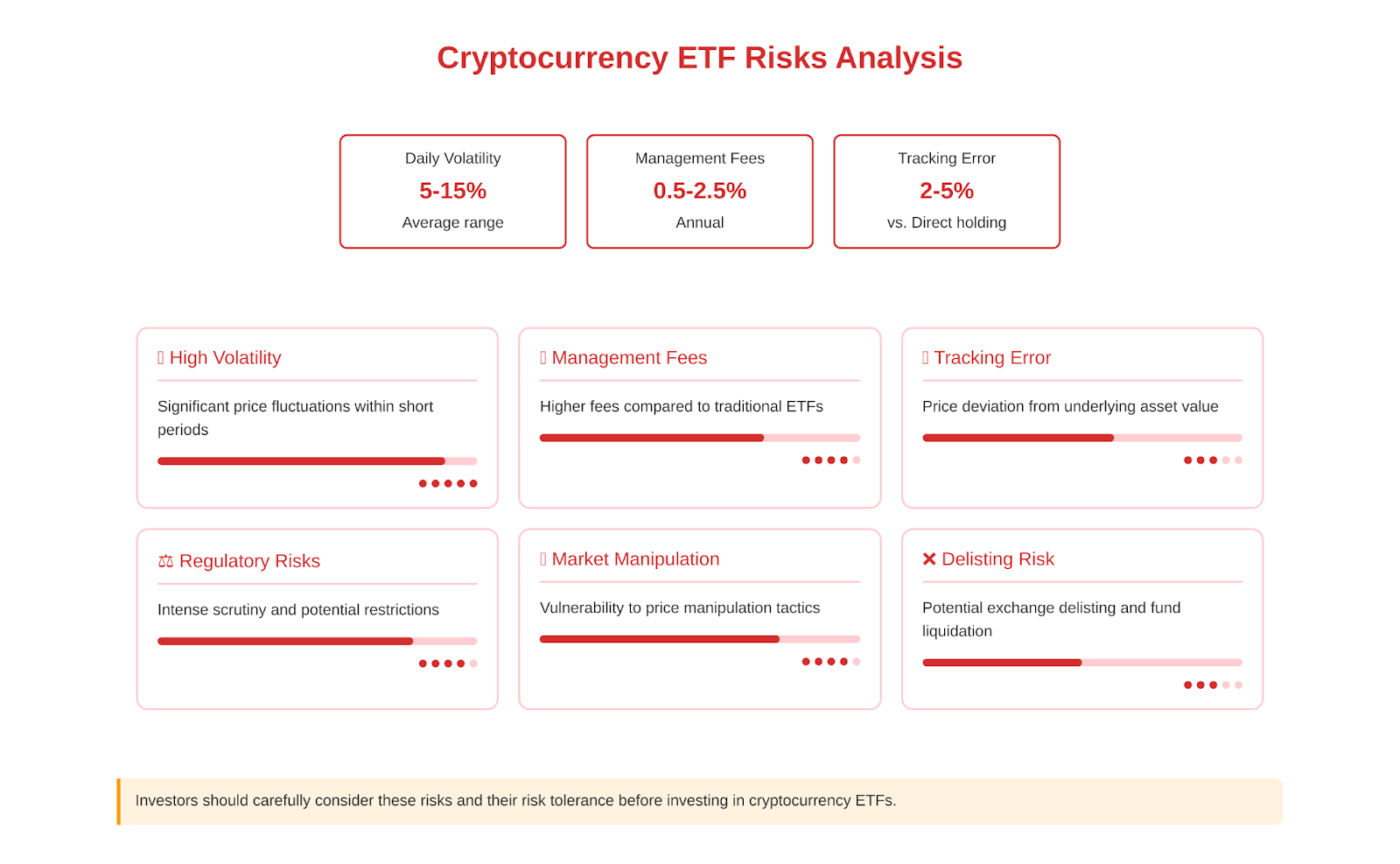
Despite the numerous benefits, investing in cryptocurrency ETFs comes with a number of risks and drawbacks that an investor should be aware of:
- High volatility. The cryptocurrency market is characterized by increased volatility compared to traditional assets. Cryptocurrency prices can show significant fluctuations within a short period of time. This is directly reflected in the dynamics of cryptocurrency ETFs, the value of which can change dramatically during a trading session. Investors in crypto-ETFs should be prepared for potentially high short-term risks.
- Management fees. Like traditional ETFs, cryptocurrency funds charge investors a management fee. It covers the costs of holding crypto assets, licensing, exchange listing and management team fees. Crypto-ETF fees are usually higher than traditional funds due to the increased complexity of dealing with crypto assets. This reduces the investor’s ultimate return.
- Tracking the underlying asset. Due to market characteristics (volatility, liquidity, regulation), the price of a crypto-ETF can deviate from the value of the underlying asset. This is especially characteristic of futures ETFs. As a result, an investor may underperform compared to owning cryptocurrencies directly, especially in a rising market.
- Regulatory risks. Cryptocurrency ETFs face intense scrutiny from financial regulators, many of whom are wary of the cryptocurrency industry. Regulatory restrictions and bans on cryptocurrency ETFs (such as the SEC’s multi-year refusals to launch bitcoin ETFs) can negatively impact the liquidity and attractiveness of these instruments to investors.
- Risk of market manipulation. The cryptocurrency market is not mature and efficient enough yet. It may be manipulated by large players (pumps, dumps, spoofing, etc.). This can distort the pricing of the underlying crypto-assets and mislead investors who focus on the dynamics of crypto-ETFs.
- Delisting risk. A cryptocurrency ETF may be delisted from an exchange if it fails to meet liquidity, regulatory or provider requirements. In this case, the fund will be liquidated and investors will receive cash compensation, which may be less than the initial investment.
Investors should carefully consider these risks and critically assess how much they are willing to accept. Cryptocurrency ETFs are high-risk instruments that are not suitable for all categories of investors. Before making an investment decision, you should read the fund’s prospectus and weigh the potential returns against the risks.
Cryptocurrency ETFs in the world
The history of the emergence of cryptocurrency ETFs is closely linked to the development of the digital asset market itself. The first attempts to launch bitcoin exchange-traded funds were made back in 2013, but they faced resistance from regulators. The breakthrough year was 2018, when the first regulated cryptocurrency ETP (exchange-traded product) Amun Crypto Basket Index was launched in Switzerland. In the following years, cryptocurrency ETFs and ETPs began to appear in other jurisdictions as well.
The regulatory environment for cryptocurrency ETFs varies from country to country:
| U.S. | The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) had long refused to launch spot bitcoin ETFs, citing risks of market manipulation. The breakthrough was the approval of the first bitcoin futures ETFs in October 2021. Now in 2025, spot and futures ETFs for bitcoin and ether are traded in the United States. |
| Europe | European countries turned out to be more open to cryptocurrency ETPs (which are not ETFs in the strict sense, but have similar characteristics). Cryptocurrency ETPs are traded on exchanges in Switzerland, Germany, Sweden, the Netherlands and Austria. However, there is no unified approach to regulation at the EU level yet. |
| Canada | Canada has become the first country to approve spot cryptocurrency ETFs. In February 2021, the Purpose Bitcoin ETF and Evolve Bitcoin ETF began trading on the Toronto Stock Exchange. Other bitcoin and ether ETFs were added later. |
| Brazil | In Brazil, the first bitcoin ETF was launched in June 2021 on the B3 stock exchange. The ETF allows investors to access bitcoin without buying the cryptocurrency directly. |
| Asia | In Asia, cryptocurrency ETFs are less common due to the tough stance of regulators. However, in countries such as Hong Kong and Singapore, it is possible to trade ETFs registered in other jurisdictions. |
Some of the most popular cryptocurrency ETFs and ETPs at the moment include:
- iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT)
- ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITO)
- ProShares Short Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITI)
- Siren Nasdaq NexGen Economic ETF (BLCN)
- Amplify Transformational Data Sharing ETF (BLOK)
With the further development of regulation and maturity of the cryptocurrency market, new cryptocurrency ETFs can be expected to appear in different countries. However, investors should carefully assess the specifics and risks of these instruments in each particular jurisdiction.
How to start investing in cryptocurrency ETFs?
- Investing in cryptocurrency ETFs is a lot like buying traditional exchange-traded funds, but has its own nuances. Here are step-by-step instructions for novice investors:
- Choosing a platform or broker. To invest in cryptocurrency ETFs, you’ll need a brokerage account. Choose a regulated broker that offers ETF trading and has access to exchanges where the cryptocurrency funds you’re interested in are traded. Pay attention to commissions, minimum account amount, convenience of the platform and quality of customer support.
- Analyze the fund before buying. Do not invest in a cryptocurrency ETF without first analyzing its key characteristics:- Underlying Asset. Find out which cryptocurrencies the fund is focused on and in what proportions they are represented in its portfolio.
- Fund structure. Figure out whether the fund is physical (holds cryptocurrencies directly) or futures (uses derivatives). This affects pricing features and risks.
- Commissions. Be sure to take into account the fund’s management fee, which will lower your final return. Compare the fees of different funds.
- Historical returns. Study what returns the fund has demonstrated in the past, but remember that past results do not guarantee future dynamics.
- Trading volume and spreads. Check the ETF’s average daily trading volume and typical spreads between the buy and sell prices. These are indicators of a fund’s liquidity.4. Diversification. Don’t put all your savings into one cryptocurrency ETF. Spread your investments among several funds or supplement your portfolio with ETFs for other asset classes (stocks, bonds, gold).
- Long-term approach. The cryptocurrency market is very volatile, so investing in crypto-ETFs is primarily suitable for long-term investors. Be prepared to hold positions for months or years and don’t panic over short-term fluctuations.
- Regular investments. Instead of investing a large amount at once, consider investing regularly in small installments. This will help average out the entry price and smooth out volatility.
- Portfolio rebalancing. Over time, the shares of different ETFs in your portfolio may change. Periodically review your portfolio structure and rebalance it according to your investment strategy.
- Follow the news. Keep up with news about the cryptocurrency market, cryptocurrency regulation, and the specific funds in which you’ve invested. But make investment decisions thoughtfully, not under the influence of emotions.
The main thing is to start investing in cryptocurrency ETFs with small amounts, gradually building up your understanding of the market and investment skills. Don’t forget that cryptocurrency investments are high-risk, so invest only the money you are willing to lose without jeopardizing your financial well-being. And be sure to diversify your investments to reduce your risks.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency ETFs offer investors new opportunities to gain exposure to the digital asset market, reducing some of the risks and technical complexities compared to buying cryptocurrencies directly. However, investing in crypto-ETFs still carries high risks due to the volatility of the underlying assets and the characteristics of the emerging market.
Choosing the right cryptocurrency ETF requires careful analysis of its structure, fees and potential risks. Investors should carefully assess their willingness to accept these risks and fit cryptocurrency ETFs into their overall investment strategy, keeping in mind the need for diversification.
The cryptocurrency ETF market is actively evolving, and new products and improved regulatory approaches can be expected in the coming years. But investors should always be guided by the principles of awareness, gradualism and adequate risk assessment when making investment decisions, especially in such a new and volatile area as cryptocurrency ETFs.