What is Bitcoin Halving and How Does It Affect Cryptocurrency Prices?

Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Bitcoin Halving
- History of Bitcoin Halvings
- Why Was Halving Introduced, and How Does It Relate to Bitcoin’s Economic Model
- How Halving Works
- How Halving Affects Bitcoin’s Price
- Theories and Analysis
- Risks and Uncertainties
- Conclusion
Introduction
Bitcoin halving is a significant event for the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Each time a halving occurs, the number of bitcoins miners receive for adding a new block to the blockchain is reduced. This phenomenon has a noticeable impact on Bitcoin’s price and the overall cryptocurrency economy. Investors and users must understand how halving affects the market, as changes in asset value and overall market conditions often accompany these events.
What Is Bitcoin Halving
Halving reduces miners’ rewards for each mined BTC block by half. As a result, fewer new coins are issued, decreasing the rate at which they enter circulation. This process is a fundamental element of Bitcoin’s economic model, limiting the total supply of circulating bitcoins.
History of Bitcoin Halvings
-
The first Bitcoin halving occurred in 2012, reducing the block reward from 50 BTC to 25.
-
The second halving occurred in 2016, lowering the reward from 25 to 12.5 BTC.
-
The third halving happened in 2020, reducing the reward to 6.25 BTC.
-
The fourth halving occurred in 2024, cutting the reward to 3.125 BTC.
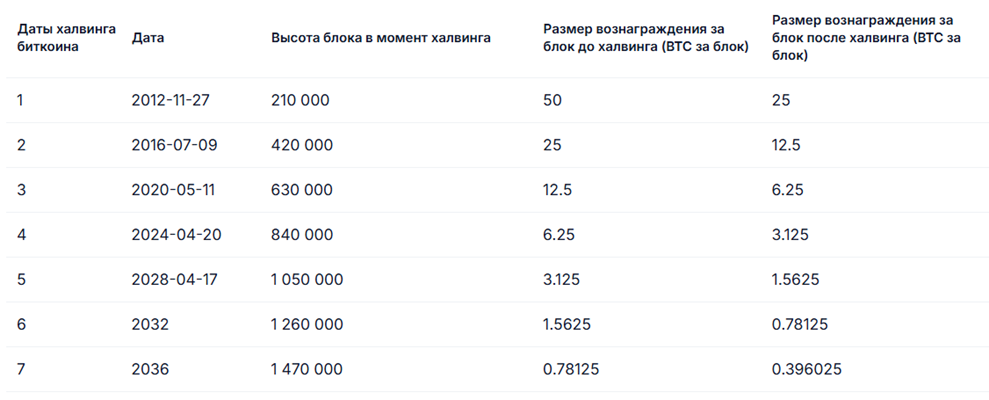
These events led to significant changes in Bitcoin’s price and overall market trends. Halving attracted the attention of investors and users, as a reduction in supply could trigger price increases.
Why Was Halving Introduced, and How Does It Relate to Bitcoin’s Economic Model
From the beginning, halving was embedded in Bitcoin’s code to create cryptocurrency scarcity. Limiting supply is a crucial aspect of value creation. The fewer bitcoins that enter circulation, the higher their price may rise if demand remains stable or increases.
Additionally, halving helps maintain Bitcoin network security. As mining rewards decrease with each halving, miners must seek new ways to sustain profitability, encouraging the development of more efficient mining technologies.
How Halving Works
Technical Aspect: Reduction of Miner Rewards
Bitcoin halving occurs every 210,000 blocks, approximately every four years. When halving happens, miners receive half the reward for mining blocks. For example, if miners earned 6.25 bitcoins per block before halving, the amount drops to 3.125 afterward. This reduction occurs automatically within the system and impacts Bitcoin’s entire economy.
Impact on Bitcoin Issuance
The total supply of bitcoins is limited to 21 million coins. This is coded into the cryptocurrency and makes Bitcoin a deflationary asset. Halving helps regulate issuance, slowing the rate of new bitcoins entering the market. With each halving, the reduction in supply becomes more noticeable.
Mining Mechanism and Its Connection to Halving
Mining is the process of adding new blocks to the blockchain and verifying transactions. Each new block contains transaction data and is created using computational power, rewarding miners for their work. Halving affects mining by reducing the reward for completed work, limiting the number of new bitcoins entering circulation.
How Halving Affects Bitcoin’s Price
Historical Relationship Between Bitcoin’s Price and Halving
Bitcoin’s price has traditionally increased after each halving. For instance, following the first halving in 2012, Bitcoin’s price surged in the following months. The same pattern occurred after the second halving in 2016 and the third in 2020.
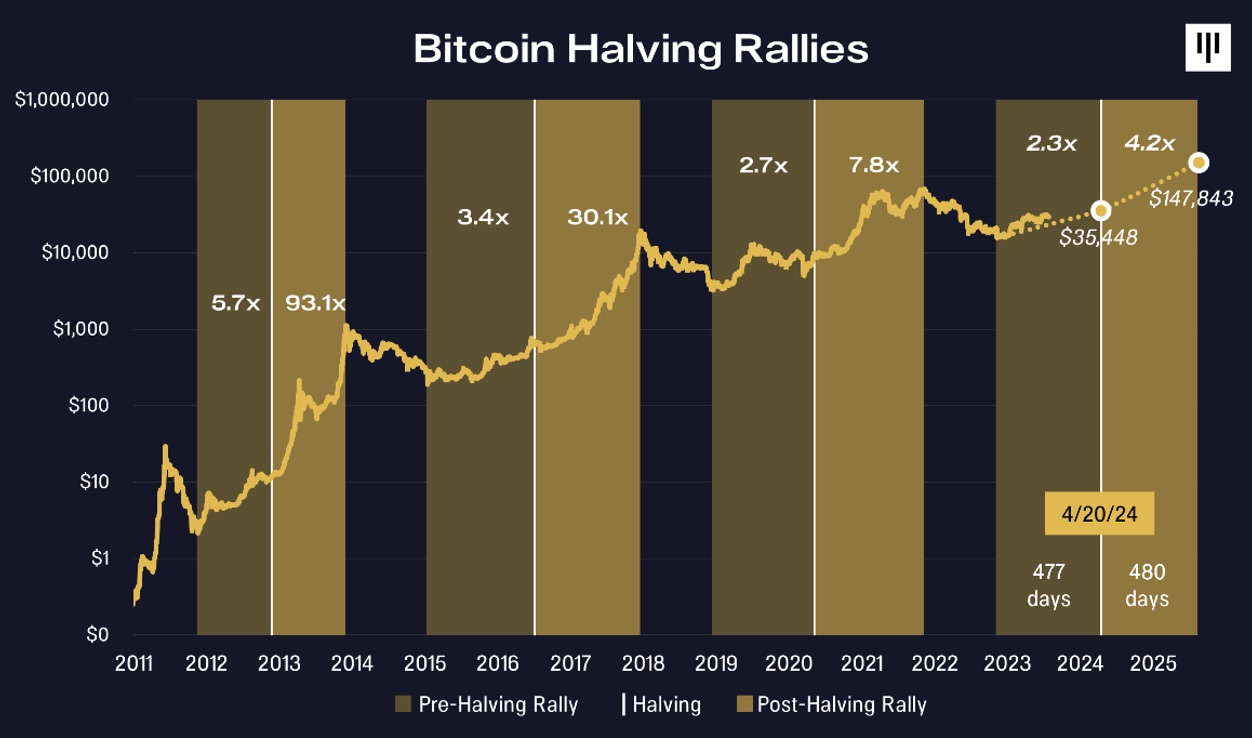
Increasing Bitcoin Scarcity and Its Effect on Market Demand
Halving creates Bitcoin scarcity, as new coin issuance slows. With a limited supply and steady or rising demand, Bitcoin’s price tends to increase. This effect is similar to markets for assets with a finite supply, where scarcity drives up value.
Market Expectations and Speculation Around Halving
Many market participants believe that halving leads to BTC price growth, fueling speculation. Investors often start buying bitcoins before halving, anticipating future gains, which can further drive demand and accelerate price increases. Such expectations usually cause market volatility, as prices may fluctuate before the event occurs.
Theories and Analysis
Bitcoin Price Forecasts After Halving
After each Bitcoin halving, the market may experience price growth. Predictions suggest that reducing the number of new bitcoins entering circulation will create scarcity, potentially driving prices higher. However, this does not always happen immediately. Some analysts believe prices may rise in the long term, while short-term volatility may occur due to shifting market sentiment.
Impact of Halving on Long-Term and Short-Term Trends
Halving can affect the market differently in the short and long term. In the short term, price movements can be unpredictable, as market participants may manipulate demand, causing volatility. However, halving typically supports price growth in the long run, as Bitcoin scarcity combined with sustained demand can increase cryptocurrency value.
Experts’ and Economists’ Opinions on Halving’s Effects on the Cryptocurrency Market
Expert opinions on halving’s consequences vary. Some economists believe halving increases scarcity and drives price growth, as limited supply creates competition for bitcoins. Others argue that Bitcoin’s price depends on numerous factors, including regulations, demand, and technological developments. Some also suggest that the next halving could differ from previous ones due to significant market changes. However, most analysts agree that halving impacts the cryptocurrency market, even if its precise effects are difficult to predict.
Risks and Uncertainties
Impact of Halving on the Mining Ecosystem
Halving can affect the mining industry, as reduced block rewards make mining less profitable for some participants. This may force less efficient mining farms to shut down, potentially lowering the network’s hash rate. However, as Bitcoin’s price rises, mining may remain profitable for larger farms, encouraging them to continue operations.
Risks to Bitcoin Network Stability
If halving reduces mining profitability for specific participants, it could impact network stability. A drop in hash rate may increase block creation time, slowing transaction confirmations. However, Bitcoin’s stability will remain strong if miners continue to support the network despite lower rewards.
Uncertainty in Price Predictions and Market Reactions
Bitcoin’s price may change after halving, but predictions remain uncertain. Even with historical data showing long-term price increases after halvings, market reactions can vary. Many factors influence price, from shifts in demand to cryptocurrency regulations. Therefore, it is impossible to accurately predict how the market will behave after the next halving.
Conclusion
Bitcoin halving remains a crucial event that significantly impacts the market and mining ecosystem. Reducing miner rewards by half helps maintain Bitcoin’s limited supply, which, in theory, should lead to price growth in the long run. However, short-term forecasts remain uncertain despite the historical correlation between halving and price increases.
The cryptocurrency market remains highly volatile, and reactions to halving can vary. It is essential to understand that halving is not a simple event that automatically drives prices up, but a complex process influenced by multiple factors determining its final effect.