Stop-loss and take-profit orders in crypto trading: what they are and how to use them

Cryptotrading is the process of trading cryptocurrencies on specialized exchanges for profit. Traders buy and sell various cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ether, Litecoin and others in an attempt to capitalize on the difference in exchange rates. Crypto trading attracts many investors with the possibility of high returns, but it also involves significant risks due to the high volatility of the market.
Risk management plays a key role in successful crypto trading. Traders must be able to control potential losses and protect their capital in a volatile market. One of the main risk management tools is stop-loss and take-profit orders.
Contents
- What is a stop-loss order?
- What is a take-profit order?
- How do I set up stop-loss and take-profit orders?
- Advantages and disadvantages of stop-loss and take-profit orders
- How to combine stop-loss and take-profit orders?
- Conclusion
What is a stop-loss order?
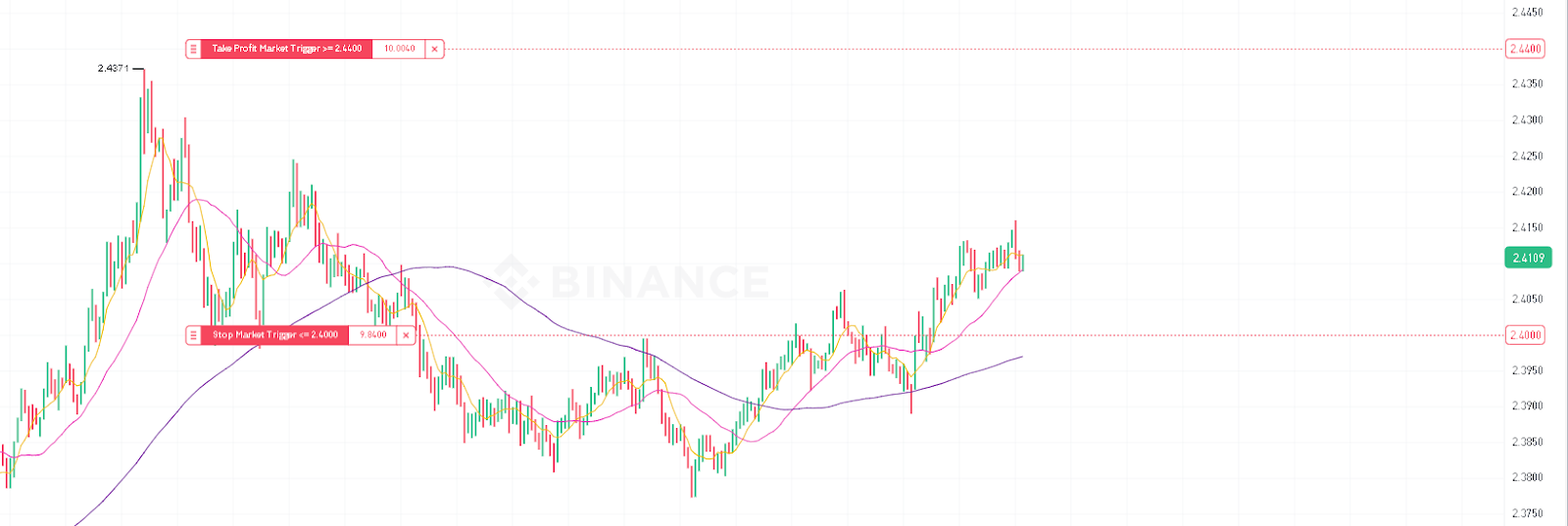
A stop-loss order is a type of stock order that is used to limit potential losses on an open position. A trader sets a stop-loss order at a certain price level, and if the price reaches this level, the order automatically closes the position, thus preventing further losses.
The way a stop-loss order works is that it turns into a market order to buy or sell when the specified price is reached. For example, if a trader bought bitcoin at $50,000 and set a stop-loss at $48,000, then when the price drops to $48,000, the order will trigger and automatically sell BTC at the current market price, limiting the trader’s losses to $2,000.
- Here are some examples of using a stop-loss order:
- A trader opens a long position in Efirium at $2000 and sets a stop-loss at $1900. If the price drops to $1900, the position will be automatically closed, limiting the loss to $100 on each Ethereum purchased.
- A trader opens a short position in LTC at $200 and places a stop loss at $210. If the price rises to $210, there will be an automatic buyback of LTC, limiting losses to $10 on each Litecoin sold.
Selecting the correct level for a stop-loss order is an important aspect of risk management. Setting a stop-loss too close to the current price may result in premature triggering of the order due to short-term market fluctuations (“noise”). On the other hand, placing a stop loss too far away can lead to excessive losses. Traders usually place stop losses at key support or resistance levels, taking into account market volatility and the size of their position.
What is a take-profit order?
A take-profit order is a type of stock exchange order that is used to automatically close a position when a specified profit level is reached. A trader sets a take-profit order at a certain price, and when the price reaches this level, the order is executed, fixing the profit on the deal.
The take-profit order helps traders to lock in profits without missing an opportunity to capitalize on a favorable price movement. When the price reaches the take-profit level, the order automatically closes the position by placing a market sell (for long positions) or buy (for short positions) order. This allows traders to realize profits without waiting for a trend reversal or price correction.
Examples of using the “take-profit” order:
- A trader buys Bitcoin at a price of $45,000 and sets take profit at $50,000. If the price reaches $50,000, the order triggers and automatically sells the Bitcoin, locking in a $5,000 profit.
- The trader opens a short position in Ripple (XRP) at $1.00 and places take profit at $0.90. When the price drops to $0.90, the order will execute, buying back XRP and locking in a $0.10 profit on each XRP sold.
Choosing the correct level for a take-profit order is an important factor in maximizing profits. Setting take-profit too close to the current price may limit the potential profit if the price continues to move in a favorable direction. On the other hand, setting take-profit too far away can result in lost profits if price reverses before reaching the level. Traders usually place take profit at key resistance or support levels, taking into account market momentum and the potential for price movement.
How do I set up stop-loss and take-profit orders?
A step-by-step guide to placing orders on a cryptocurrency exchange:
- Log in to your cryptocurrency exchange account and go to the trading page of the selected trading pair (e.g. XRP/USDT).
- Determine the desired position entry price and place a limit or market order to buy or sell.
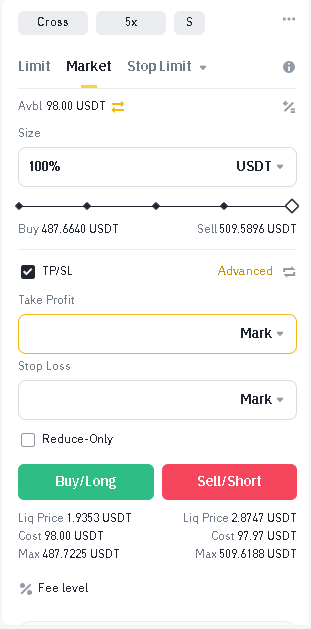
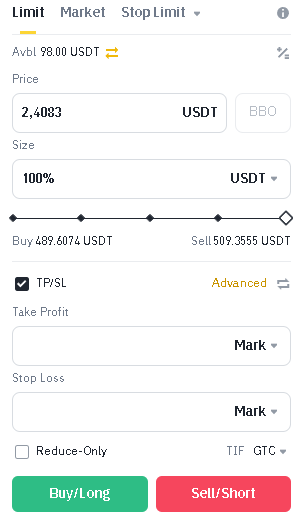
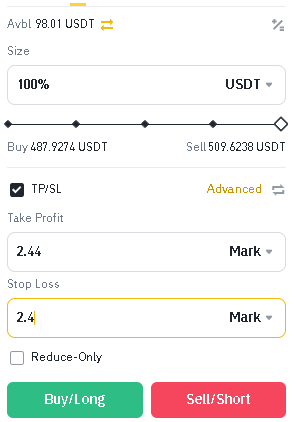
- To set a “stop-loss” order, enter the desired activation price in the corresponding field. This will be the price at which your position will be automatically closed to limit losses.
- To set a “take-profit” order, enter the desired activation price in the corresponding field. This will be the price at which your position will be automatically closed to lock in profits.
- The exchange will process your request and set the specified orders. Your position will now be automatically closed when the set stop-loss or take-profit levels are reached.
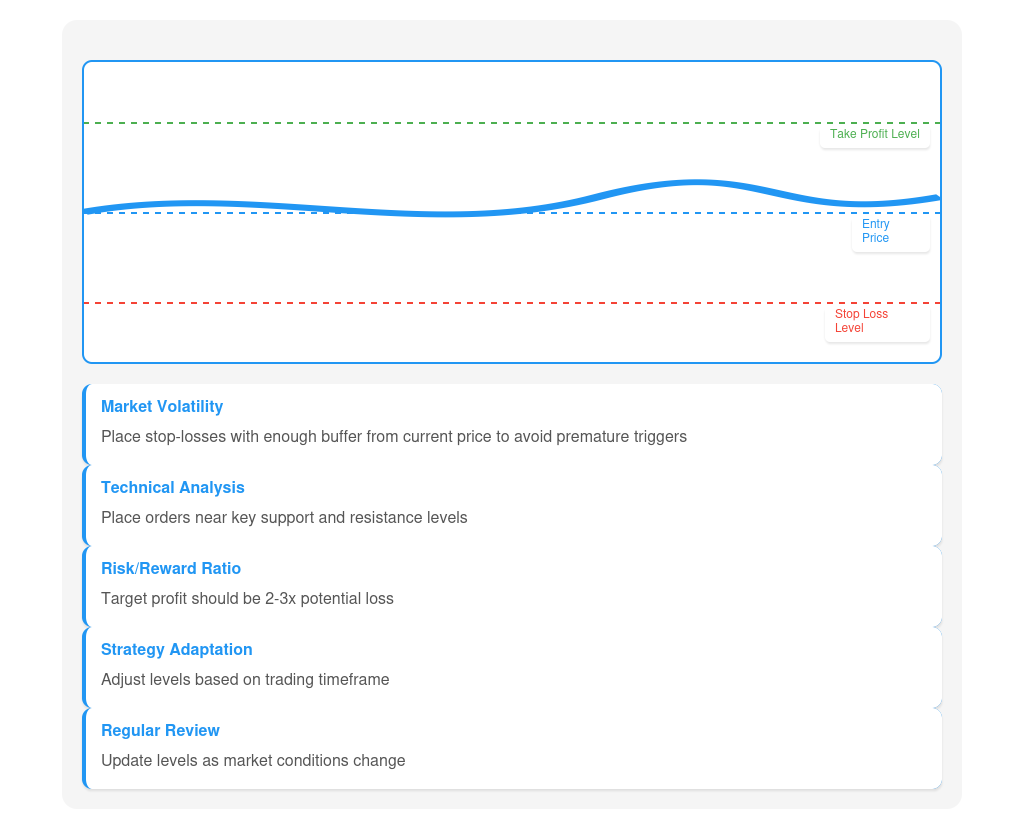
Tips on choosing optimal levels for orders:
- Consider market volatility: In a volatile market, place stop-losses far enough away from the current price to avoid accidental triggering due to short-term fluctuations.
- Use technical analysis: Identify key support and resistance levels on the chart and place stop-loss and take-profit near these levels.
- Consider the risk/reward ratio: Set stop-loss and take-profit levels so that the potential profit is at least 2-3 times the potential loss.
- Adapt the levels to your strategy: If you are using a short-term strategy, set stop-loss and take-profit levels closer to each other. For long-term strategies, these levels can be more distant.
- Review the levels regularly: As the market develops and conditions change, adjust the stop-loss and take-profit levels to match the current situation.
Advantages and disadvantages of stop-loss and take-profit orders
Advantages
- Process automation: Stop-loss and take-profit orders allow to automate the process of closing positions when certain price levels are reached. This saves traders from having to constantly monitor the market and manually close positions, which is especially convenient for those who cannot devote much time to trading.
- Protection against strong market movements: Setting stop-loss orders helps to limit potential losses in case of unfavorable price movements. If the market suddenly turns against an open position, a stop-loss order will automatically close it, preventing further losses. This is especially important in the volatile cryptocurrency market, where prices can change very quickly.
Disadvantages
- Opportunities for slippage: In conditions of high volatility and low market liquidity, slippage can occur when an order is executed at a price that differs from the price specified in the order. This occurs due to rapid price movements and the gap between the buy and sell prices. As a result of slippage, a trader can close a position at a less favorable price than planned.
- Failure to account for market changes in real time: Stop-loss and take-profit orders are set in advance and do not take into account changes in market conditions in real time. If new factors affecting price (e.g., important news or changes in market sentiment) appear after the orders are set, these orders will not be able to automatically adapt to the new conditions. Traders need to manually adjust order levels to account for the new information.
Despite these disadvantages, the advantages of using stop-loss and take-profit orders usually outweigh the possible risks. Competent use of these tools in combination with a well-thought-out trading strategy and risk management can significantly increase the efficiency and profitability of crypto trading.

How to combine stop-loss and take-profit orders?
Strategies for combining orders to minimize risk and maximize profit:
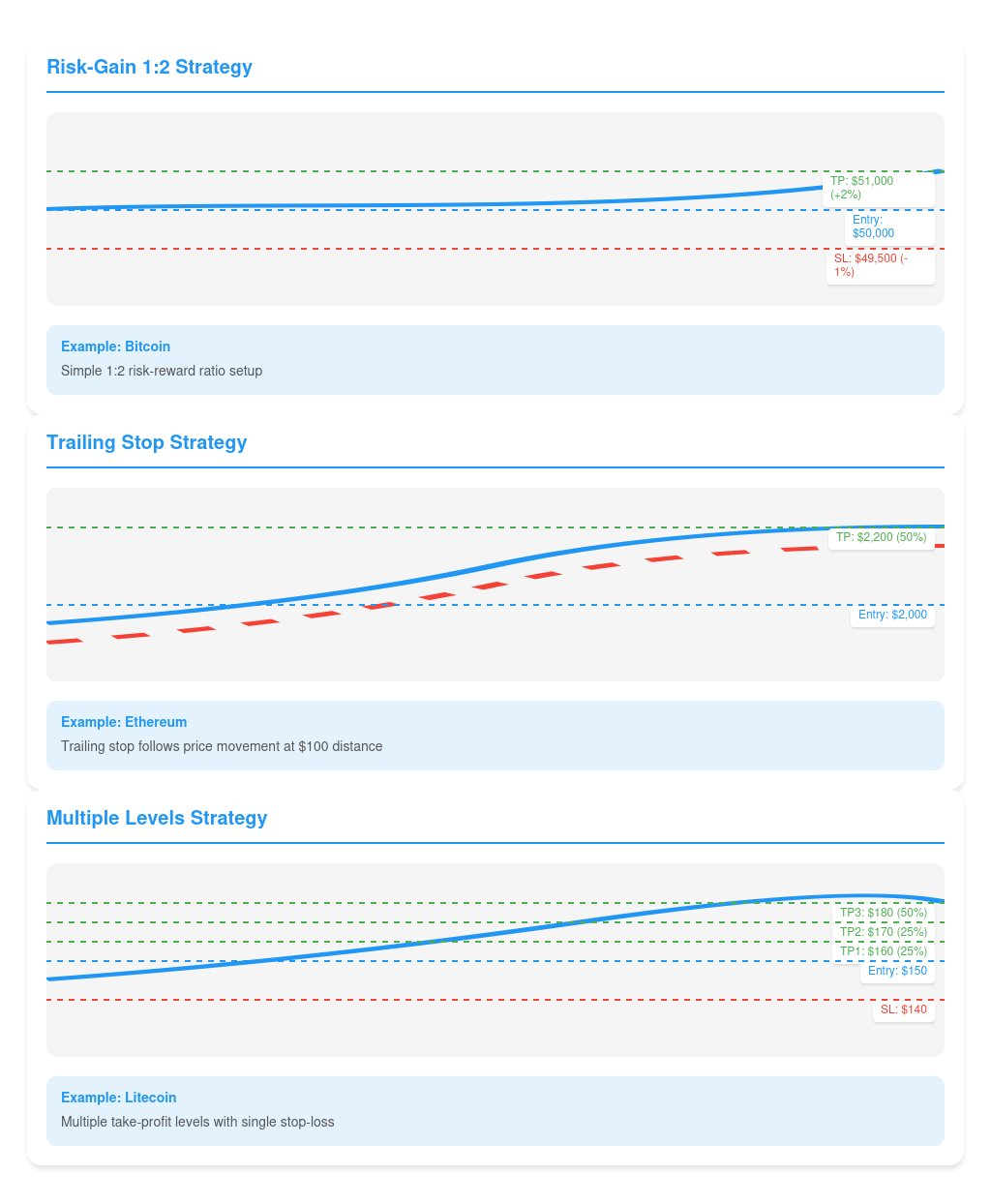
- Risk-Gain 1:2 strategy: Set the stop-loss order at a level that limits the potential loss to 1% of your trading capital, and the take-profit order at a level that provides a potential profit of 2% of your capital. This way, each successful trade will generate twice as much profit as the potential loss in case of failure.
Example: You buy bitcoin at $50,000, set the “stop-loss” at $49,500 (1% risk) and the “take-profit” at $51,000 (2% potential profit).
- Trailing Stop Strategy: Use a “take-profit” order to lock in a portion of profit when a certain level is reached, and set up a “stop-loss” order as a trailing stop that will follow the price at a set distance. This will allow you to lock in a portion of profit and at the same time give you the opportunity to make additional profits if the price continues to move in your favor.
Example: You buy Ethereum at $2000, set a “take-profit” at $2200 (locking in 50% of the position) and a trailing stop at a distance of $100 from the maximum price reached. If the price reaches $2200, half of the position will be closed and the trailing stop will follow the price, protecting your profit.
- Multiple Levels Strategy: Place multiple take-profit orders at different levels to gradually lock in profits as the price rises. Place a stop-loss order at a level that limits the overall risk of the position.
Example: You buy Litecoin at $150 and place three “take-profit” orders: at $160 (closing 25% of the position), $170 (closing another 25%), and $180 (closing the remaining 50%). You place a “Stop-loss” at $140, limiting the maximum loss to 6.7% of the position amount.
These strategies of combining stop-loss and take-profit orders help traders to manage risk, lock in profits and adapt to different market situations. However, it is important to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all strategy. Traders need to select and customize strategies according to their goals, risk appetite and the characteristics of the assets being traded.
Conclusion
Stop-loss and take-profit orders are important tools for risk management and profit maximization in crypto trading. Proper use of these orders helps traders to limit potential losses, lock in profits and automate the trading process. Combining stop-loss and take-profit orders according to a well thought-out strategy allows you to optimize trading results and adapt to different market conditions.