Stablecoin: what it is and why it's important for the cryptocurrency ecosystem

In recent years, cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies have become one of the most discussed topics in the world of finance and investment. This innovative industry is developing rapidly, attracting the attention of both enthusiasts and skeptics. One of the key elements of the cryptocurrency ecosystem is stablecoins – digital assets designed to provide stability and reliability in the volatile world of cryptocurrencies.
Contents
- What is stablecoin?
- Types of stablecoin
- Why are stablecoins important to the cryptocurrency ecosystem?
- Benefits of stablecoin
- Risks and challenges of stablecoin
- The future of stablecoin
- Conclusion
What is stablecoin?
Stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency designed to minimize the price volatility common to most cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. The value of a stablecoin is pegged to the value of another asset, usually a fiat currency (such as the U.S. dollar or euro) or commodity (such as gold). This pegging ensures that the price of the stablecoin is stable relative to the underlying asset.
The way stablecoin works is that behind each issued stablecoin is a reserve of the underlying asset. For example, if a stablecoin is pegged to the U.S. dollar at a 1:1 ratio, there should be one U.S. dollar in reserve for each issued stablecoin. This provides users with the confidence that they will always be able to exchange their stablecoins for fiat currency at a fixed rate.
There are two main varieties of stablecoins: centralized and decentralized.
- Centralized Stablecoins are issued and managed by a centralized entity, such as a company or bank. This organization is responsible for holding the reserves and ensuring that the issued stablecoins match the amount of reserves. Examples of centralized stablecoins are Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC).
- Decentralized stablecoins, on the other hand, operate based on smart contracts on the blockchain without the involvement of a centralized entity. They are backed by other cryptocurrencies or algorithms that automatically regulate the supply of stablecoins to maintain a stable price. An example of a decentralized stablecoin is DAI, which is backed by the Ethereum cryptocurrency and managed by smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.

Types of stablecoin
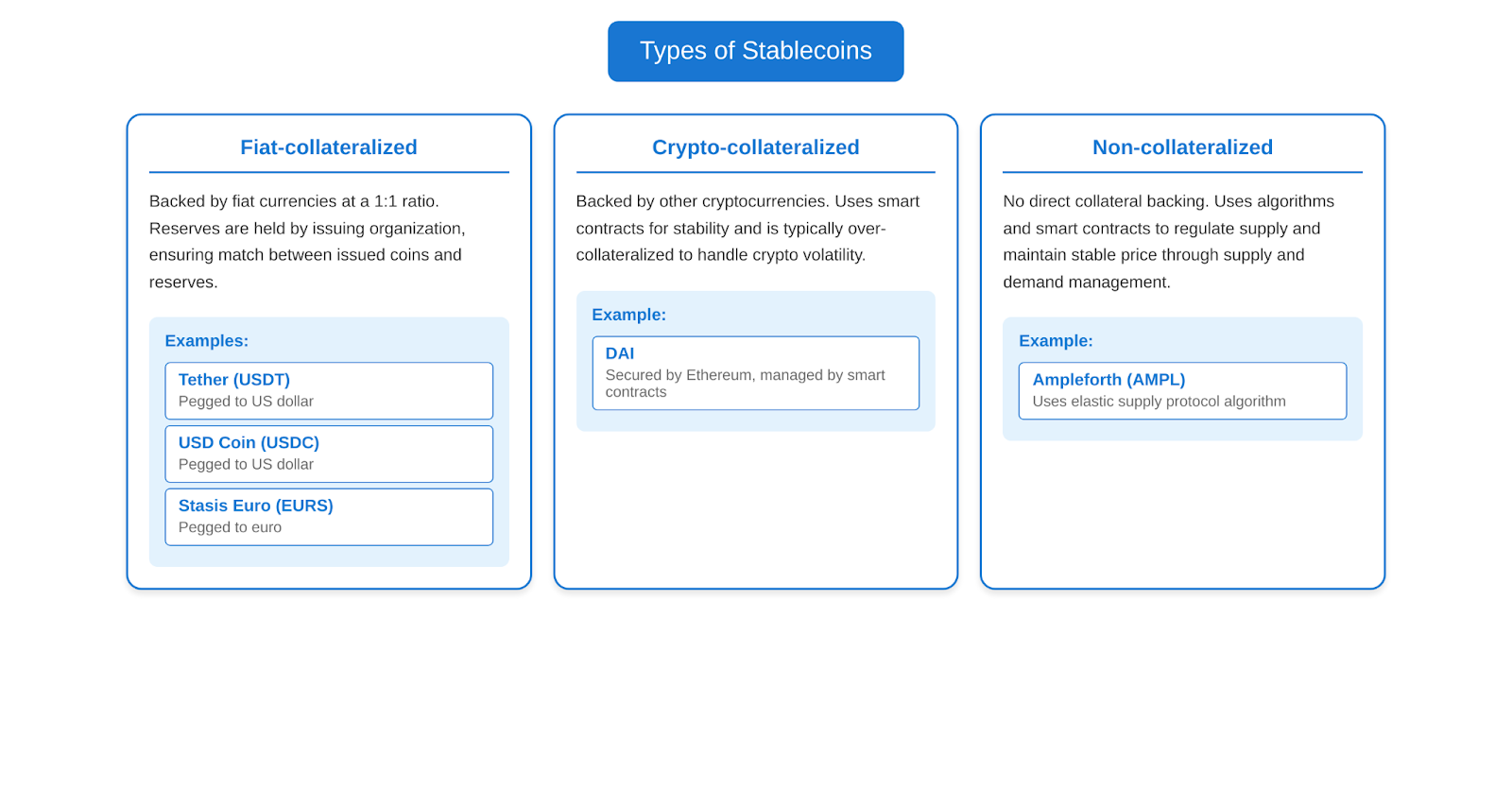
There are three main types of stablecoins, each with its own characteristics and stability mechanisms: Fiat-collateralized, Crypto-collateralized, and Non-collateralized.
Fiat-collateralized stablecoins
This type of stablecoin is backed by fiat currencies, such as the US dollar or euro, at a 1:1 ratio. An equivalent amount of fiat currency is held in reserve for each issued stablecoin. The company or organization issuing the stablecoin is responsible for holding the reserves and ensuring that the number of issued stablecoins matches the amount of reserves.
Examples of stable coins backed by fiat:
- Tether (USDT) – pegged to the US dollar
- USD Coin (USDC) – pegged to the US dollar
- Stasis Euro (EURS) – pegged to the euro
Crypto-collateralized stablecoins
This type of stablecoin is backed by other cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum or Bitcoin. Smart contracts are used to maintain a stable value of the stablecoin, which automatically regulate the provision and issuance of the stablecoins. Since cryptocurrencies themselves are volatile, crypto-collateralized stablecoins are usually over-collateralized to compensate for possible price fluctuations of the securing cryptocurrencies.
Example Crypto-collateralized stablecoin:
- Example DAI – secured by the Ethereum cryptocurrency and managed by smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
Non-collateralized stablecoins
This type of stablecoin does not have collateral in the form of fiat currencies or cryptocurrencies. Instead, they rely on algorithms and smart contracts to regulate the supply of Stablecoins and maintain a stable price. These algorithms automatically adjust the amount of Stablecoins in circulation based on supply and demand, similar to how central banks manage the money supply.
Example Non-collateralized stablecoin:
- Ampleforth (AMPL) – uses an “elastic supply protocol” algorithm to adjust the number of tokens in circulation in response to changes in demand, aiming to maintain a stable price around $1.
Each type of stablecoin has advantages and disadvantages related to the level of decentralization, transparency, and potential risks. The choice of stablecoin type depends on the specific needs of users and their confidence in the various stability mechanisms.
Why are stablecoins important to the cryptocurrency ecosystem?
Stablecoins play a vital role in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, solving a number of problems and opening up new opportunities for users, investors, and developers. Here are a few key reasons why stablecoins are so important:
- Reducing Volatility: A Role in Cryptocurrency Market Stabilization
One of the main problems with the cryptocurrency market is the high price volatility. The value of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum can fluctuate significantly over a short period of time, making it difficult to use them as a reliable means of exchange or store of value. Stablecoins solve this problem by providing price stability and reducing market volatility. By being linked to fiat currencies or other assets, stablecoins offer the stability and predictability needed for wider adoption of cryptocurrencies.
- Application in DeFi (decentralized finance): Providing liquidity, credit and other services
Stablecoins play a key role in the development of the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. DeFi platforms use stablecoins to provide liquidity, lending and other financial services without the involvement of traditional financial institutions. Users can deposit their stablecoins into liquidity pools on DeFi platforms, receiving interest or rewards in return. Stablecoins are also widely used as collateral for loans and in other financial instruments such as derivatives and insurance products.
- Transactional Convenience: Ease and speed of use in everyday transactions
Stablecoins offer users a simple and fast way to make transactions, both within the cryptocurrency ecosystem and beyond. Due to their stable value and peg to fiat currencies, stablecoins can be used for everyday purchases, remittances, and other financial transactions without worrying about price volatility. Transactions with stablecoins are usually faster and cheaper than traditional wire transfers, making them an attractive alternative for international payments and microtransactions.
- Role in preserving value: Hedging risks for investors and traders
Stablecoins serve as an important tool for hedging risk and preserving the value of cryptocurrency assets. In times of high market volatility, investors and traders can convert their cryptocurrencies into stablecoins to protect their capital from potential losses. Stablecoins are also used as a middle ground when trading between different cryptocurrencies, allowing traders to quickly exit volatile positions without having to convert to fiat currencies.
Benefits of stablecoin
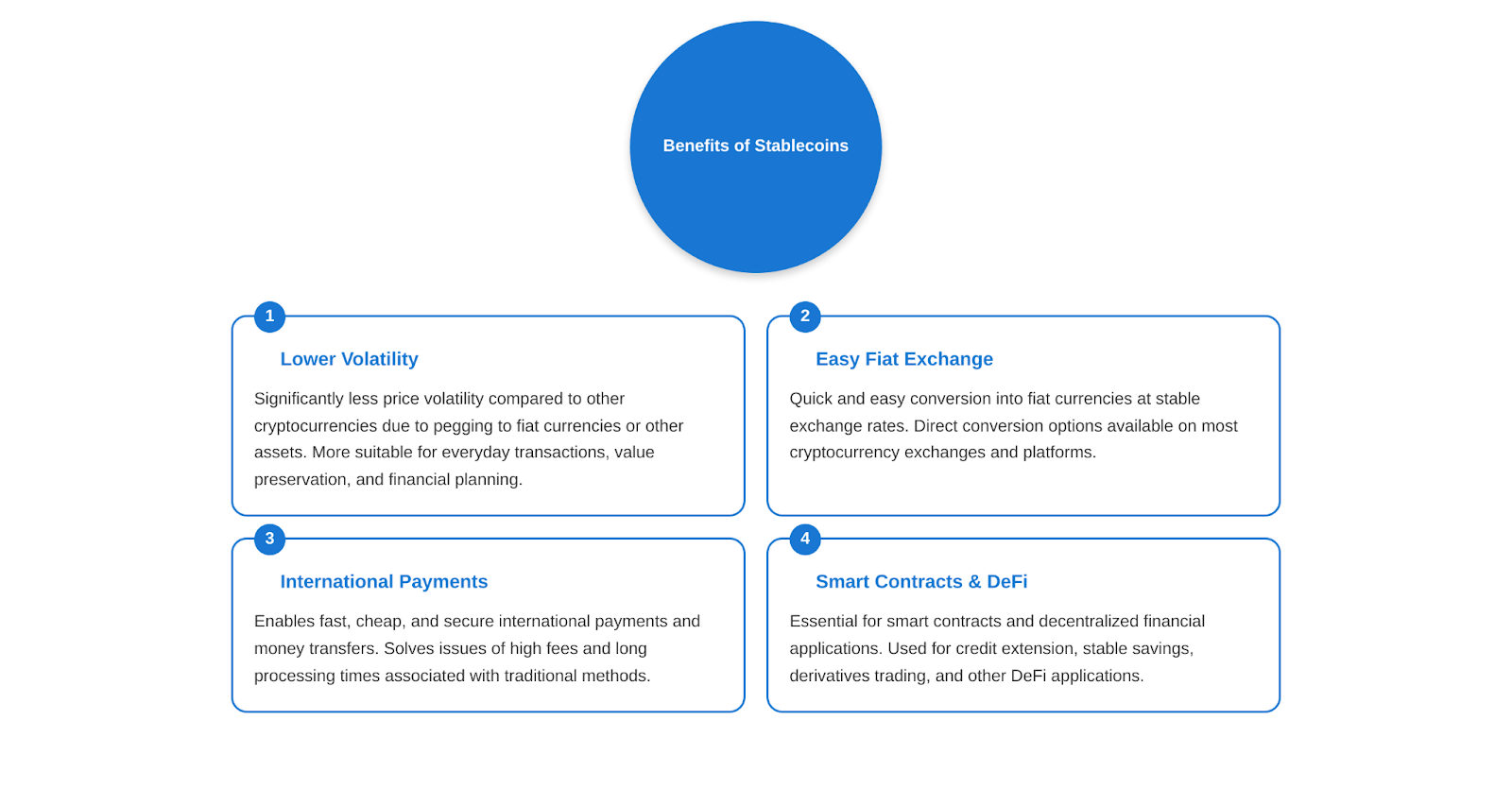
Stablecoins have a number of advantages that make them attractive to users, investors, and developers in the cryptocurrency ecosystem. Here are some of the key advantages of stablecoins:
- Lower volatility compared to other cryptocurrencies
The main advantage of stablecoins is their stability compared to other cryptocurrencies. Due to their pegging to fiat currencies or other assets, stablecoins exhibit significantly less price volatility. This makes them more suitable for everyday transactions, value preservation, and financial planning. Users can hold stablecoins without worrying about the sudden price fluctuations that characterize Bitcoin or Ethereum.
- Ease of exchange for fiat money
Another important advantage of Stablecoins is their ease of exchange into fiat currencies. Most stablecoins can be quickly and easily converted into US dollars, euros, or other fiat currencies at a stable exchange rate. This is especially convenient for users who need to move frequently between cryptocurrencies and fiat money. Many cryptocurrency exchanges and platforms offer direct conversion between stablecoins and fiat currencies, which simplifies the exchange process.
- Possibilities of use in international payments and money transfers
Stablecoins open up new opportunities for fast, cheap and secure international payments and money transfers. Traditional methods such as wire transfers or payment systems often involve high fees, long processing times and limitations on transaction amounts. Stablecoins solve these problems by providing almost instant transactions with minimal fees. This is especially relevant for cross-border payments and money transfers to countries with less developed financial infrastructure.
- Applications in smart contracts and financial applications
Stablecoins play an important role in the functioning of smart contracts and decentralized financial applications (DeFi). Smart contracts are self-executing computer programs that automatically perform certain actions when specified conditions are met. Stablecoins are often used as a medium of exchange and settlement in smart contracts, providing stability and predictability to financial transactions. In DeFi applications, stablecoins are used to extend credit, create stable savings, trade derivatives, and more.
Risks and challenges of stablecoin
Despite the many benefits, stablecoins also come with certain risks and challenges that investors, users, and regulators need to consider. Here are some of the major risks and challenges associated with stablecoins:
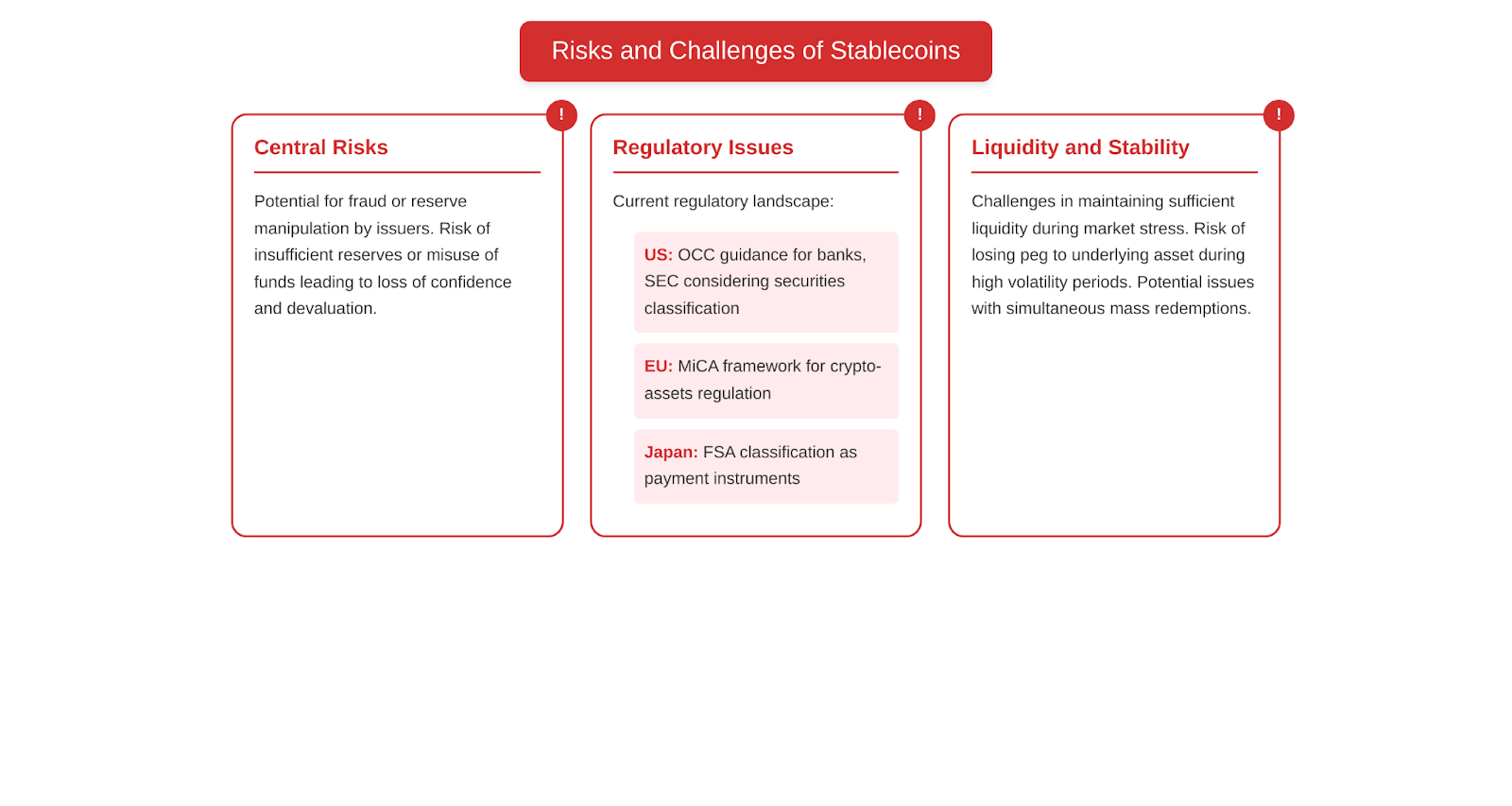
- Central risks (e.g. fraud or reserve manipulation)
One of the main risks of centralized stablecoins is the possibility of fraud or manipulation of reserves by the issuer. Because centralized stablecoins rely on trust in the company or entity issuing them, there is a risk that the issuer may act in bad faith, for example, by not providing the stablecoins with sufficient reserves or using the reserves for other purposes. This could lead to a loss of confidence in Stablecoin and its devaluation.
- Regulatory issues: which countries have already started to regulate stablecoin?
Regulation of stablecoins is a pressing issue in many countries. Governments and financial regulators are trying to find a balance between supporting innovation and protecting consumers from potential risks. Some countries have already started to develop a legal framework for regulating stablecoins:
- US: The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) has issued guidance allowing banks to issue and transact in stablecoins. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is also considering regulating stablecoins as securities.
- European Union: The European Commission has proposed a comprehensive regulatory framework for cryptoassets, including stablecoins, as part of its “Regulation on Markets in Crypto-Assets” (MiCA) project.
- Japan: Japan’s Financial Services Agency (FSA) has classified stablecoins as payment instruments and requires issuers to obtain a remittance license.3. Liquidity and stability issues
Another challenge for stablecoins may be maintaining sufficient liquidity and stability during periods of market stress. If a large number of users simultaneously attempt to redeem their stablecoins, the issuer must have sufficient reserves to meet this demand. If reserves are insufficient or frozen, this could lead to a loss of confidence and stability in the stablecoin.
In addition, even with sufficient reserves, stablecoins may face challenges in maintaining a peg to the underlying asset. For example, during periods of high market volatility, stablecoins may temporarily lose their peg and trade at a premium or discount to the target price.
The future of stablecoin
Stablecoins have great potential for further development and integration into various aspects of the financial system and digital economy. Let’s take a look at some of the key areas and prospects for the development of stablecoins:
- Prospects of development and implementation of stablecoin in traditional financial systems
As stablecoins become more popular and established, their gradual integration into traditional financial systems is expected. Banks, payment systems, and other financial institutions may begin to utilize stablecoins to improve their services, reduce costs, and speed up transactions. Partnerships between stablecoin issuers and traditional financial institutions may lead to the creation of innovative financial products and services that combine the advantages of cryptocurrencies with the stability of fiat money.
- Potential for central banks adopting central bank digital currencies (CBDCs)
Many central banks around the world are actively exploring the possibility of issuing their own digital currencies (CBDCs). CBDCs are essentially stablecoins issued and backed by central banks. They can provide the benefits of cryptocurrencies, such as efficiency, transparency and accessibility, while maintaining the stability and trust inherent in fiat currencies. CBDC implementation can encourage further development and adoption of stablecoins, creating a more favorable regulatory environment and increasing public confidence in digital currencies.
- The role of stablecoin in the development of Web3 and decentralized financial ecosystems
Stablecoins play a key role in the development of decentralized financial (DeFi) ecosystems and the broader concept of Web3. Web3 is a vision of a more decentralized, open and secure internet in which users have greater control over their data and digital assets. Stablecoins serve as an important component of the Web3 infrastructure, providing a stable means of exchange and settlement in decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts.
As the DeFi ecosystem evolves and new innovative protocols and platforms emerge, the demand for stablecoins will grow. They will be used to provide liquidity, loan origination, derivatives trading and many other financial services in a decentralized environment. The integration of stablecoins into Web3’s identity, reputation and risk management solutions can also contribute to a safer and more secure ecosystem.
Conclusion
Stablecoins represent an important innovation in the world of cryptocurrencies, providing stability, ease of use, and broad applicability. Due to their advantages, stablecoins are contributing to the wider adoption of cryptocurrencies, the development of decentralized finance and integration with traditional financial systems.
Despite the existing risks and challenges related to regulation, collateralization and liquidity, stablecoins have great potential to transform the financial landscape. Their further development and adoption, including in the context of central bank digital currencies and the Web3 ecosystem, opens new horizons for innovation and increased access to financial services.
The future of stablecoins looks promising, and as challenges are overcome and regulatory frameworks evolve, they could become an integral part of the global financial infrastructure, providing users around the world with a stable, efficient and affordable way to store and transfer value.